Fun Facts!!
Discover amusing and mind-blowing fun facts that will surprise you!
– 9 Interesting Facts About Garter Snakes
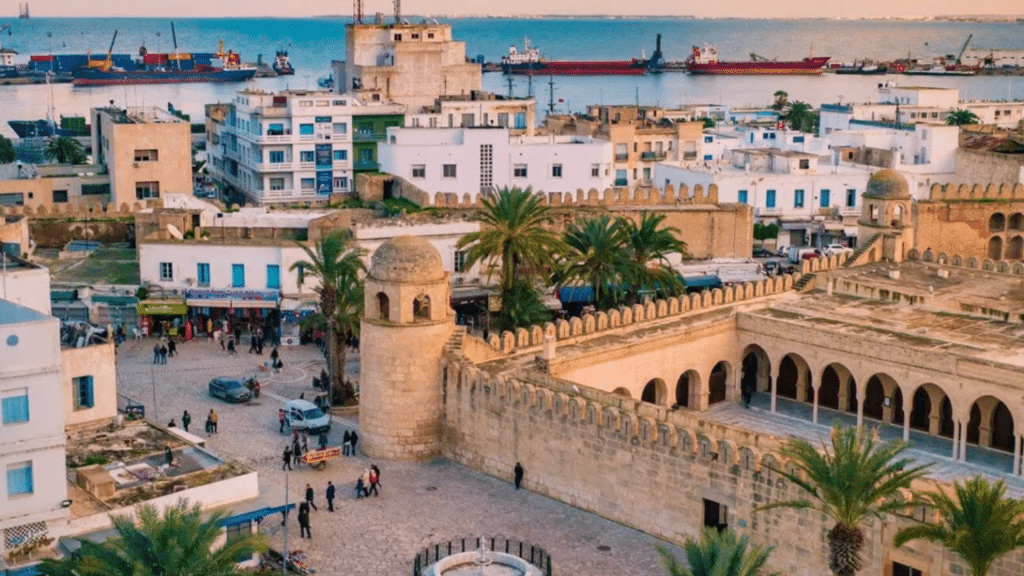
– 29 Interesting Tunisia Fun Facts to Know
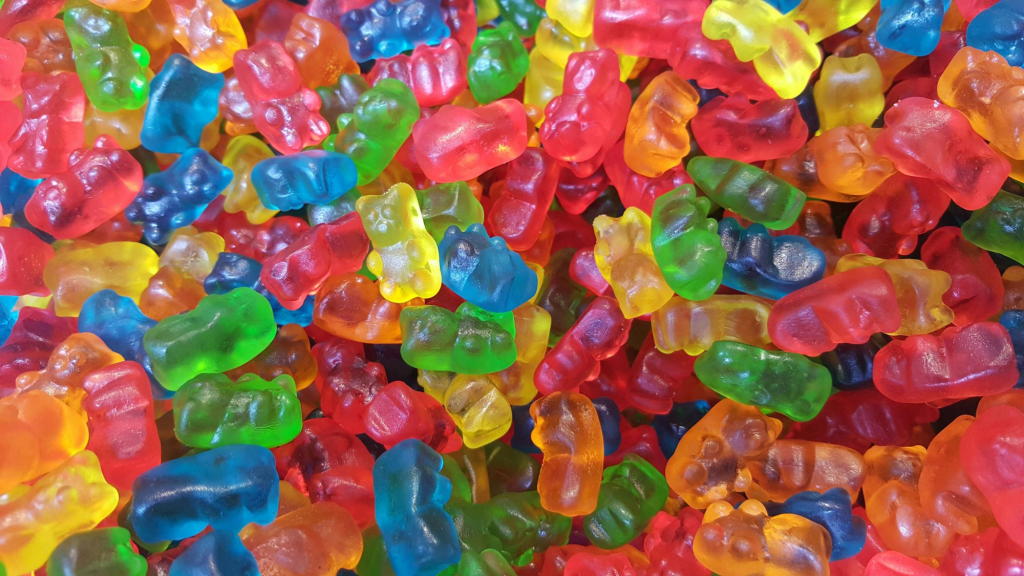
– 25 Facts About Gummy Bears
– 31 Fun Facts About Latvia Culture and History
Latest Posts
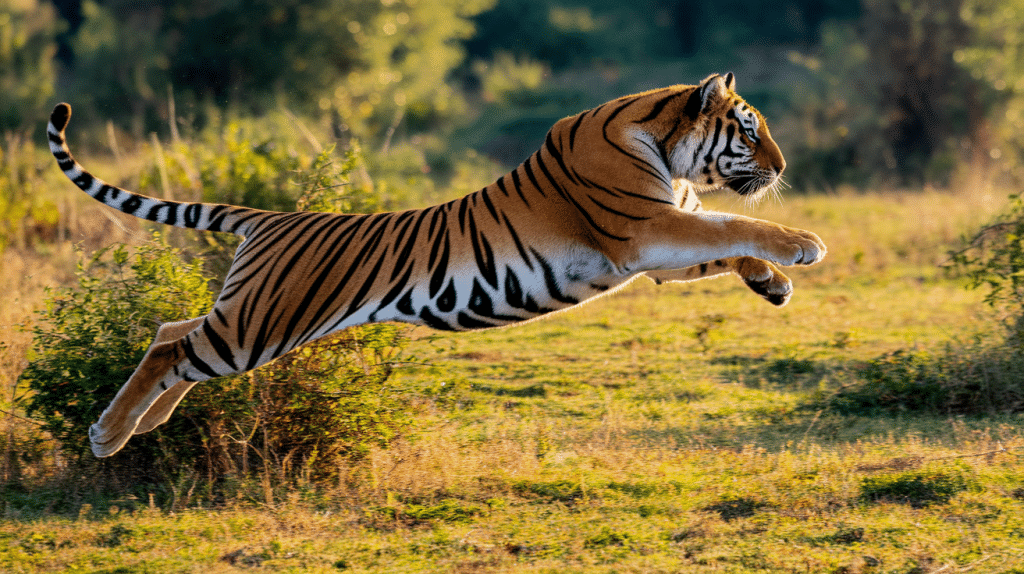
Tigers are known for their beauty and strength, but one ability often......
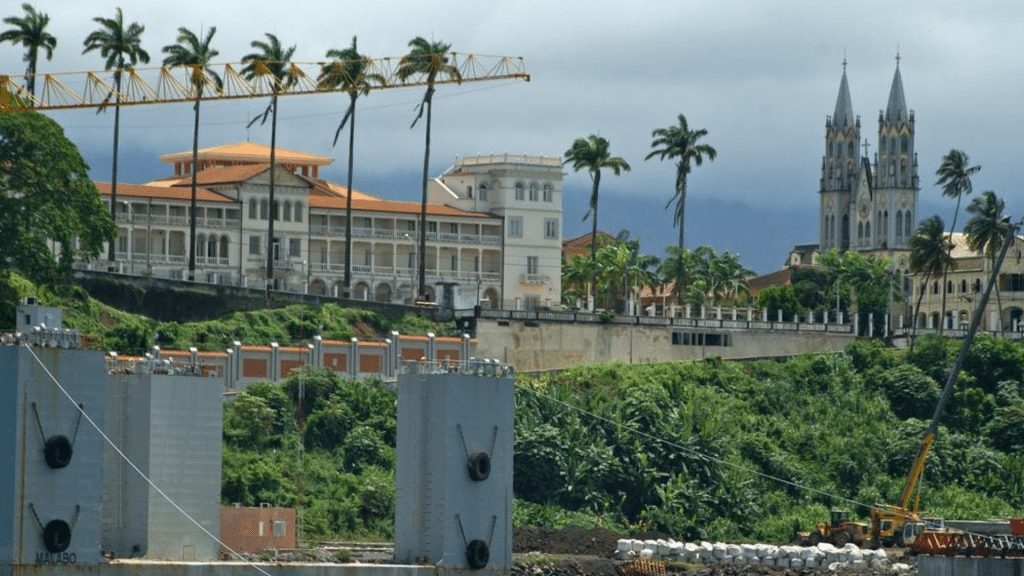
Have you ever heard of a country in Africa where Spanish is......
Have you ever stopped to think about why gummy bears are so......
Tunisia is a country with layers of history, culture, and everyday life......

Welcome to Some Interesting Facts
SomeInterestingFacts.com was founded in 2012 by curious minds eager to share fascinating discoveries. Originally interns and freelancers, we worked behind the scenes learning from the site's founders. Over time, the founders moved on, passing the torch to us. Today, we proudly serve as the site's main curators. Our goal: ignite curiosity and uncover hidden stories. We explore history, technology, life, and more. We honor the original vision while bringing fresh perspectives. For over 13 years, we’ve loved surprising our readers. Join us in this ongoing journey of learning and wonder. Want to know more? Visit our About Us page!
Step into the wild and uncover the secret lives of animals across the globe. From jungle predators to arctic wanderers, we explore how creatures think, survive, and interact. Learn about animal emotions, intelligence, and instincts in ways that will surprise you. Whether it's migration mysteries or pack dynamics, each post brings nature closer to you.
Discover the tiny creatures that rule our world in ways we often overlook. From buzzing bees to glowing fireflies, our blogs explore the fascinating lives of insects. Learn how they build, communicate, defend, and survive in diverse environments. Whether it’s pollination power or strange insect behaviors, there’s so much more to bugs than meets the eye.
Explore the wonders of science — from mind-blowing physics to everyday chemistry — in simple, engaging ways. Discover how science shapes our world, from nature and tech to health and space.
Find A Posts
Nature & ecosystem
Discover the beauty and balance of nature, where every organism plays a role in the web of life. From lush forests to fragile coral reefs, explore how ecosystems function, adapt, and sustain our planet.
Geography Facts
Explore the world one fact at a time! From towering mountains to hidden deserts, discover fascinating insights about Earth’s landscapes, countries, and natural wonders. Perfect for curious minds who love maps, places, and global trivia.
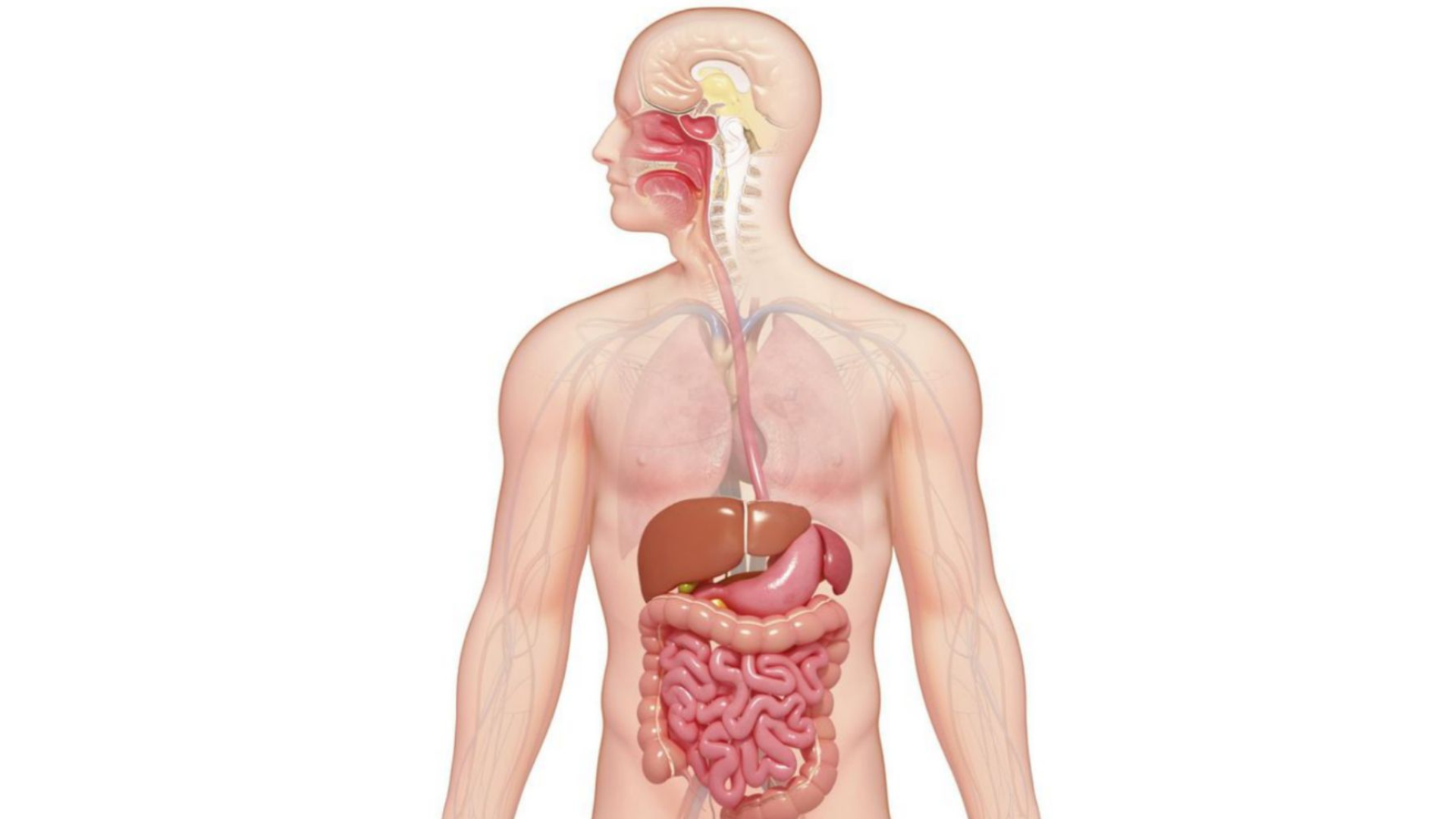
Human Body
Explore the incredible mechanics of the human body — from organ functions to the mysteries of the brain. Dive into fascinating facts about anatomy, health, and how our systems work together. Uncover what keeps us alive, moving, and thriving every single day.
Birds
When you see a big bird flying high in the sky, it......
Many people wonder about owls during cold winters. As temperatures drop and......
Have you ever spotted wild turkeys during the day but wondered where......
Have you ever noticed large, rectangular holes in tree trunks while walking......