Elephants stand as the largest land mammals on our planet today. These massive creatures command attention not only for their size but also for their extraordinary physical abilities.
However, among the many aspects of elephant biology that merit scientific attention, their bite mechanics offer an interesting area of study for researchers.
While many know elephants for their trunk strength and powerful legs, fewer people understand the significant force these animals can generate with their jaws.
So, let’s get into the elephant’s bite force and some of its interesting facts in detail below.
Physical Characteristics of Elephant Jaws
The jaw of an elephant might not look attractive at first glance, especially compared to predators with visible fangs.
However, these herbivores possess a specialized oral structure that is specifically designed for their plant-based diet.
An elephant’s jaw moves primarily in a forward and backward motion rather than the side-to-side chewing that humans perform.
This straight-line grinding action helps them break down tough plant material with maximum efficiency.
Their jaw muscles, while not as visibly prominent as those in big cats contain remarkable strength necessary for processing huge quantities of vegetation daily.
Comparison of African vs. Asian Elephant
| Feature | African Elephants | Asian Elephants |
|---|---|---|
| Mouth Size | Larger mouths | Smaller oral structures |
| Ear Shape | Diamond-shaped ears | Smaller, rounder ears |
| Head Shape | More angular | More rounded |
| Upper Lip Structure | Less pronounced | Creates a distinctive profile visible from a distance |
| Tusks | Present in both males and females | Typically, only males develop prominent tusks |
| Average Size | Larger (up to 13,000 lbs) | Smaller (up to 11,000 lbs) |
| Habitat | Savannas and forests of sub-Saharan Africa | Forests of South and Southeast Asia |
Understanding Elephant Bite Force
African elephants can exert a bite force of approximately 400 pounds per square inch (psi). This is a modest figure when compared to many other large mammals.
And, Asian elephants show similar measurements, with bite forces typically ranging between 350-380 psi.
Comparing Elephant Bite Force to Other Animals
Animal Bite Forces (PSI) from Strongest to Weakest:
- Orca (Killer Whale): ~19,000 PSI – Strongest bite in the animal kingdom
- Sperm Whale: ~15,000 PSI – Second strongest bite force
- Nile Crocodile: 5,000 PSI – Strongest bite among reptiles
- Great White Shark: 4,000 PSI – Powerful oceanic predator bite
- Saltwater Crocodile: 3,700 PSI – Massive reptilian jaw strength
- Alligator: 2,980 PSI – Formidable bite for crushing prey
- Hippopotamus: 1,800 PSI – Strongest bite among land mammals
- Gorilla: 1,300 PSI – Very strong for its size
- Hyena: 1,100 PSI – Built for crushing bones
- Tiger: 1,050 PSI – Top big cat bite force
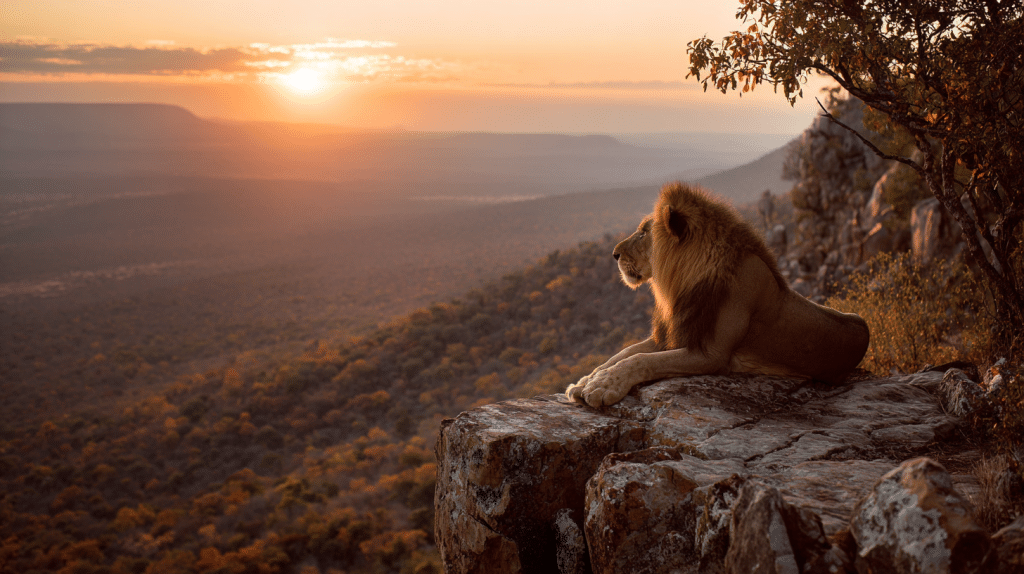
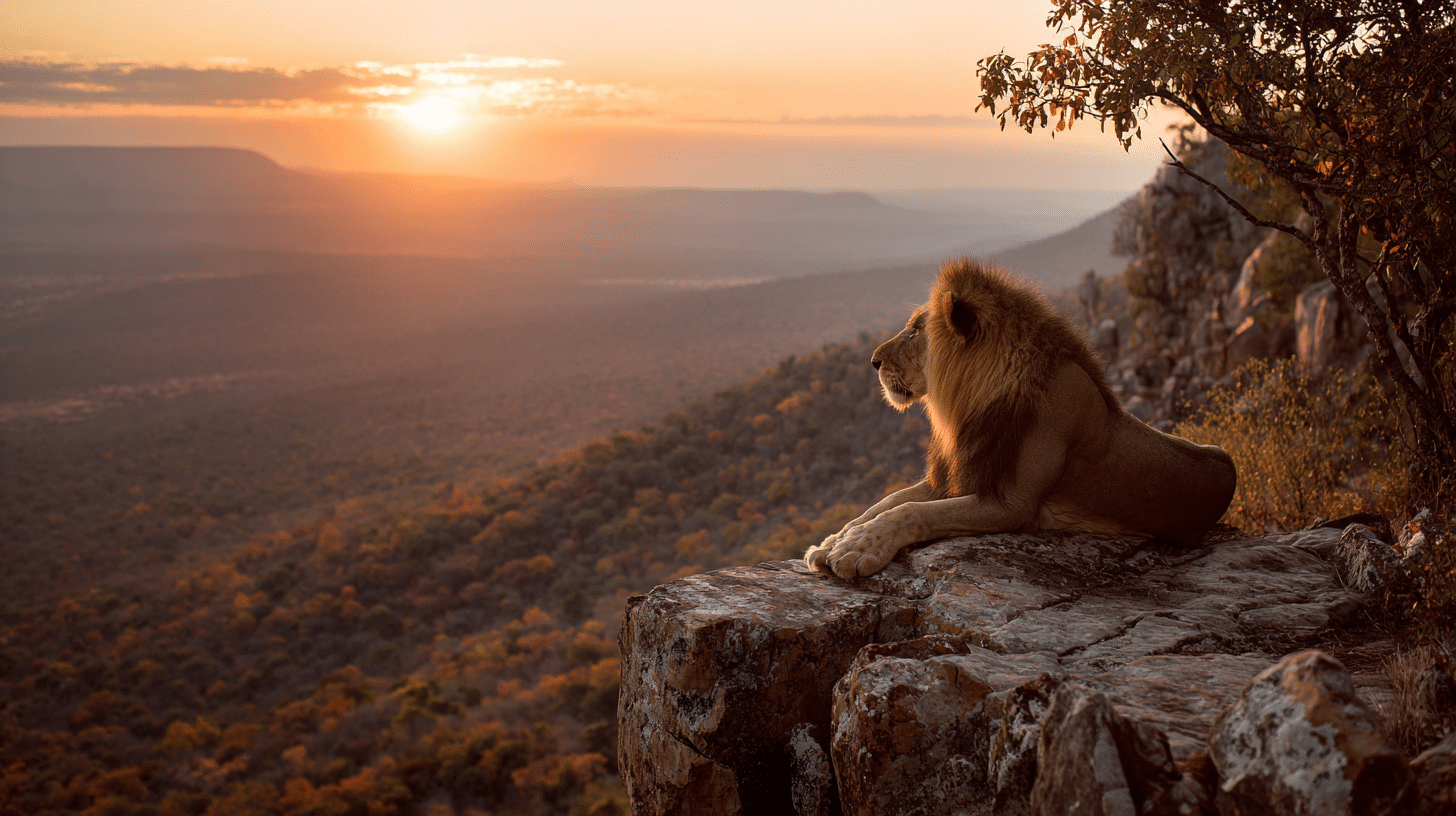
- Lion: 650 PSI – Strong but less than tigers
- Human: ~162 PSI – Relatively weak compared to other mammals
How Do Elephant Trunks Help Their Biting Abilities?
The elephant’s trunk serves as a crucial addition to its oral capabilities. This highly mobile organ contains approximately 40,000 muscles, allowing elephants to grasp food with remarkable precision.
While elephants use their teeth for crushing and grinding vegetation, their trunks perform the initial food gathering and preparation.
However, the coordination creates an efficient feeding system that compensates for limitations in their dental structure.
The trunk essentially functions as a mobile upper lip and nose combination. It extends the elephant’s reach and handling capacity, allowing them to collect, prepare, and transfer food to their mouth for processing.
Interesting Facts About Elephants

Below are some interesting facts about elephants, highlighting their intelligence, emotional complexity, and remarkable physical abilities that make them truly unique within the animal kingdom.
- Elephants can recognize themselves in mirrors, demonstrating self-awareness that is rare among animal species.
- An elephant’s trunk contains over 40,000 muscles and can lift objects weighing up to 700 pounds.
- Elephants communicate through sounds too low for humans to hear
- Baby elephants suck their trunks for comfort, similar to how human babies suck their thumbs
- Elephants mourn their dead and may even return to the remains of family members years later
- The skin of an elephant can be up to 1 inch thick, yet it’s sensitive enough to feel a fly landing
- Elephants can smell water from up to 12 miles away and often dig wells that other animals use
Conclusion
Always remember that elephants are quite interesting animals, renowned for their strength, intelligence, and emotional complexity.
They form tight family bonds, communicate in unique ways, and display problem-solving abilities.
Along with that, their impressive size and specialized anatomy enable them to thrive in their environments, but it’s their gentle nature and social connections that truly stand out.
As research grows, you get to gain more insight into how these animals communicate, think, and feel. This knowledge helps you better protect them and their habitats for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Animal has 19000 Psi Bite Force?
The Orca (Killer Whale) has a bite force of approximately 19,000 PSI, making it the animal with the strongest bite force currently known.
How Many Species of Elephants Exist Today?
There are three living elephant species: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant.
Do Elephants Use Their Bite Force Often?
No. Elephants rarely use biting as a means of defense or attack. They rely more on their trunks, tusks, and massive size when threatened.