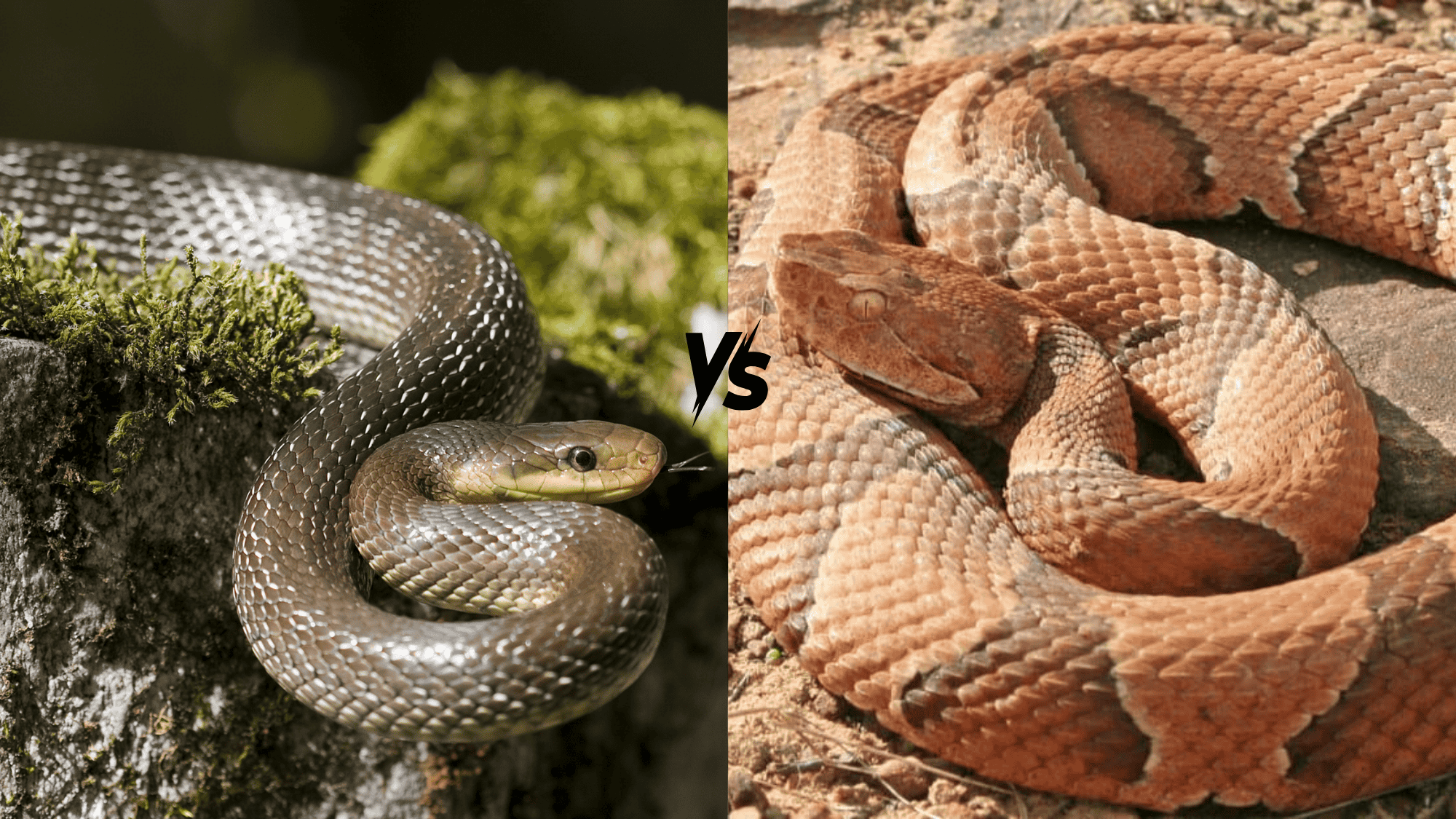
Snakes often stir up fear when spotted in yards or on hiking trails.
Two common species that are confused are the rat snake and the copperhead.
Why does knowing the difference matter?
One of these snakes helps humans by controlling pests, while the other requires careful attention due to its potential harm.
This blog will walk you through what makes each snake unique, its behaviors, and how to differentiate one from another.
With the right knowledge, your outdoor activities can become more enjoyable and less stressful in areas where these snakes live.
Difference Between Rat Snake and Copperhead
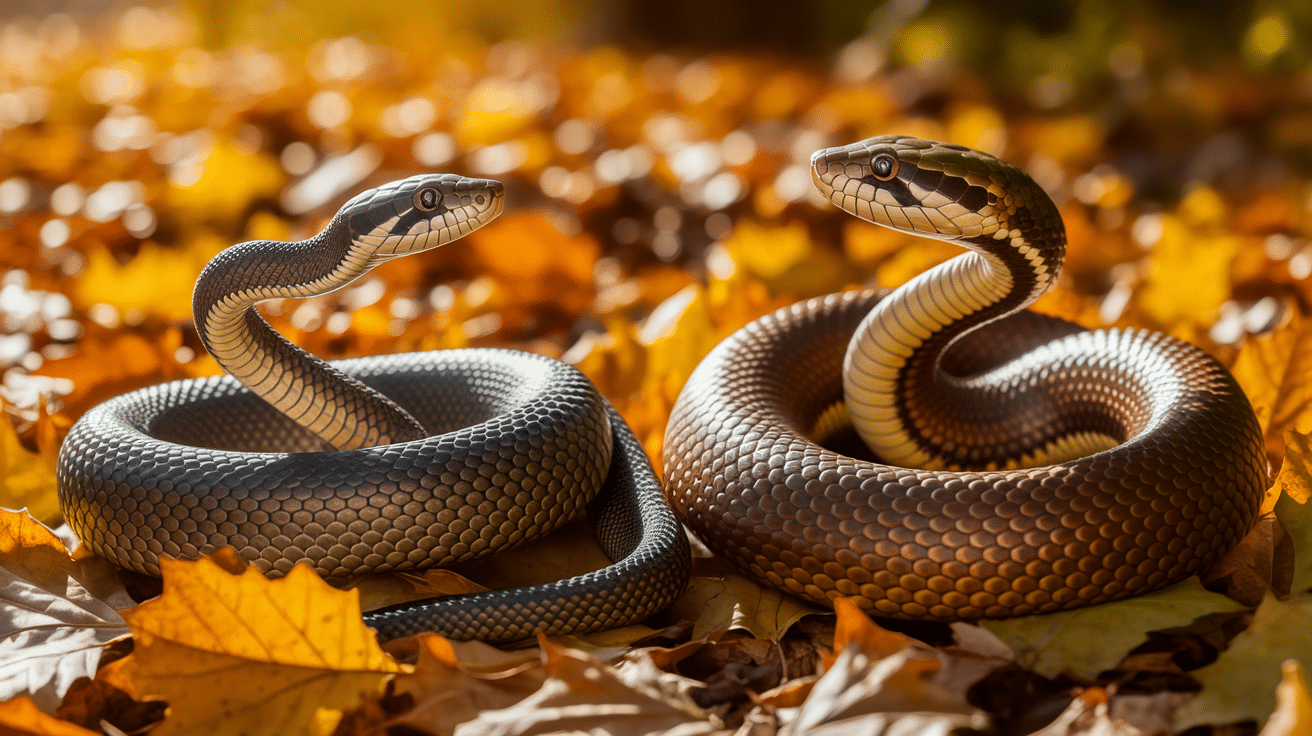

Telling rat snakes from copperheads takes some practice, but several clear differences exist between these two snake species.
Here are the major differences to help you identify them correctly:
1. Head Shape
The head shape provides one of the most reliable ways to tell these snakes apart:
- Rat Snakes: Rounded, oval-shaped head that blends smoothly with their neck
- Copperheads: A distinct triangular head that’s much wider than their neck
This difference becomes most noticeable when viewing the snake from above.
The rat snake appears streamlined, while the copperhead shows a clear widening where the head meets the neck.
2. Color Patterns
| Snake Type | Base Color | Pattern | Special Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat Snake | Black, Gray, Yellow, or Brown | Faint blotches that may fade with age | Some adults look almost solid-colored |
| Copperhead | Tan or Copper | Hourglass/bow-tie shaped bands | The pattern resembles Hershey’s kisses from the side |
3. Eye Pupils
Examining the eyes provides a quick way to distinguish these snakes from one another.
Rat snakes have round pupils that resemble black circles, similar to those of human eyes.
These round pupils are common in non-venomous snakes.
Copperheads have vertical slit pupils that look like a cat’s eye. This eye shape is typical of many venomous snakes.
Of course, this method requires getting close enough to see the eyes, which isn’t always safe.
4. Body Length
Body length varies considerably between these species:
- Adult Rat Snakes: 4 to 6 Feet Long (some Reach Over 7 Feet)
- Copperheads: 2 to 3 feet in total length
- Even large copperheads rarely exceed 3.5 feet
- The length difference is obvious when seeing adults side by side
5. Body Build
The overall body shape of these snake types differs significantly. Rat snakes have a slim, sleek body that maintains a similar thickness throughout. They look more athletic and less bulky.
Copperheads have a stockier, more muscular build with a thicker midsection. Their body appear more heavy-set and robust.
This thickness gives copperheads a stronger, more powerful look compared to the graceful rat snake.
6. Behavior
Rat Snakes
- Excellent climbers, often found in trees, barns, and attics
- Strong swimmers who cross water bodies with ease
- May shake their tails or release musky odor when threatened
- More likely to flee than fight
Copperheads
- Prefer staying on ground level
- Hide under rocks, logs, or leaf piles
- Swim when needed, but rarely climb high
- Often freezes in place when disturbed
- This freeze response leads to many accidental encounters
7. Venom Status
| Snake Type | Venom Status | Hunting Method | Bite Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rat Snake | Non-Venomous | Constriction (squeezing) | Minor Pain, Basic Wound Care |
| Copperhead | Venomous (hemotoxic) | Venom Injection | Tissue Damage, Swelling, Requires Medical Care |
8. Facial Pit
Rat snakes have a smooth face with no special openings beyond their nostrils. Their face looks clean and simple.
Copperheads, like all pit vipers, have small heat-sensing pits located between their eyes and nostrils.
These special organs detect heat from warm-blooded prey, even in darkness.
This feature functions like thermal vision, enabling the snake to locate food and evade threats.
9. Scale Texture
The texture of scales provides another clue:
Rat Snake Scales
- Smooth and glossy
- Lie flat against the body
- Give a shiny appearance in sunlight
Copperhead Scales
- Keeled with tiny ridges down the center
- create a rougher, less shiny texture
- Help with traction and quiet movement
10. Tail Tip
Young rat snakes may have patterned bodies, but their tails resemble the rest of their bodies, lacking bright coloration.
Moreover, young copperheads feature bright yellow or greenish tail tips that fade as they mature. This bright tail serves as a lure, attracting curious small prey, such as frogs or lizards.
The baby copperhead wiggles its colorful tail tip to mimic a worm or insect, bringing food within striking range.
Similarities Between Rat Snake and Copperhead
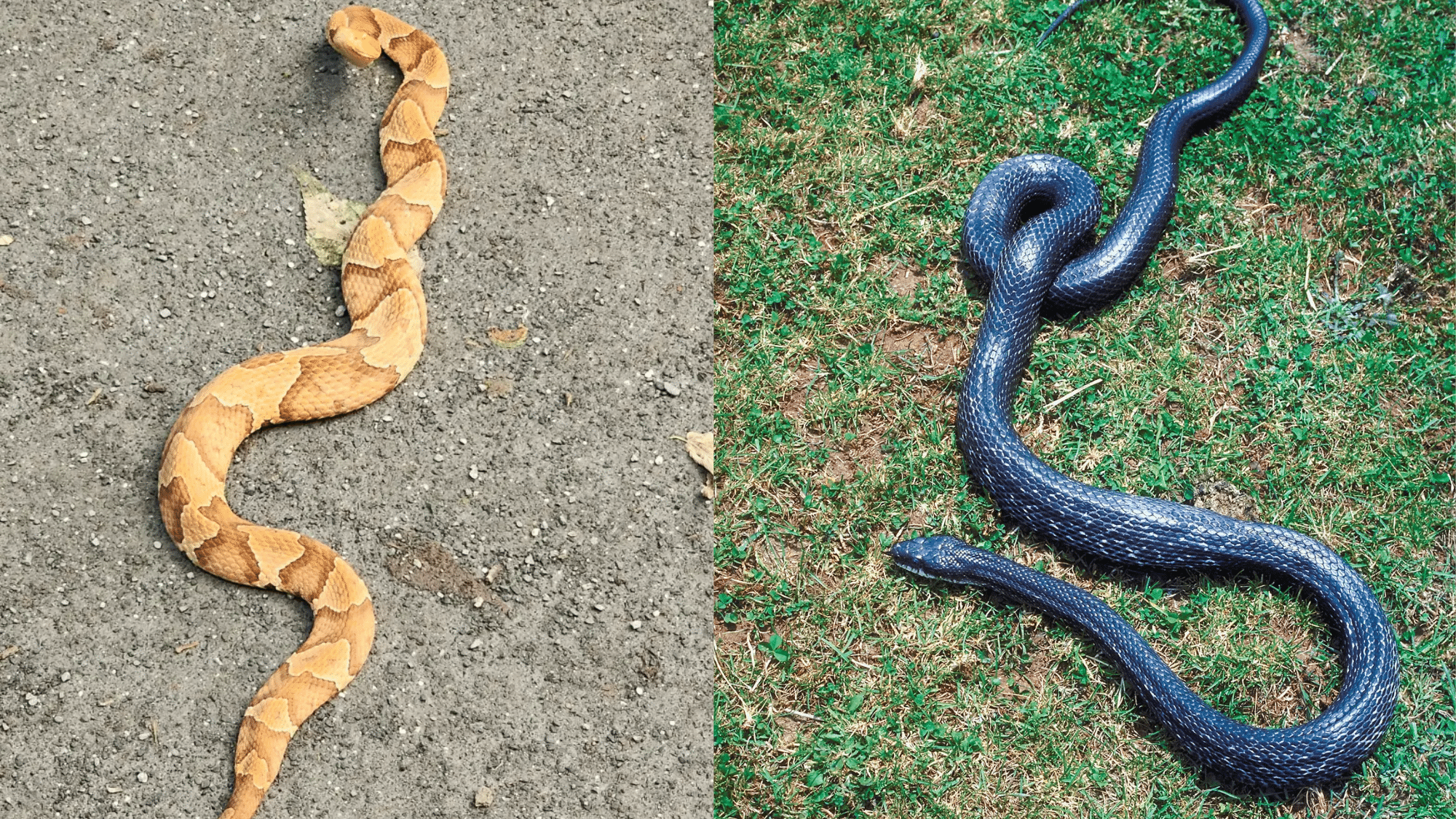

Despite their many differences, rat snakes and copperheads share several traits that can make them look alike at first glance. These shared features often confuse people who spot them in the wild.
Both snakes have similar habitats and can be found in wooded areas, rocky outcrops, and near water sources.
They favor similar environments, making it possible to encounter either species while hiking through the same terrain.
Their hunting patterns also overlap somewhat. Both target small mammals, such as mice and rats, as their primary food sources.
This shared diet means they often occupy the same ecological niche, controlling rodent populations in their areas.
Physical Similarities
- Both species can show brown or tan coloration at certain life stages
- Both have scale patterns that create texture on their bodies
- Both shed their skin as they grow
- Both have similar overall snake shapes to untrained eyes
Behavioral Traits
- Both species are mostly active during warm months
- Both hibernate during cold winter periods
- Both can freeze when first spotted by humans
- Both may produce a defensive posture when threatened
Defensive behaviors create another area of similarity. When cornered, both species might coil their bodies, vibrate their tails, and strike if they feel threatened.
Their reproductive methods match, as well. Both species lay eggs rather than giving birth live, like some other snake species.
This shared approach to reproduction represents another way these otherwise different snakes follow similar life patterns.
Understanding these similarities helps explain why people often mistake one for the other, but the differences outlined earlier remain more important for proper identification and safety.
Bonus Tip: Next time you spot a snake, take a moment, safely, to observe its features.
In a rat snake vs copperhead encounter, look for head shape: rat snakes have a rounded head, while copperheads show a distinct triangle.