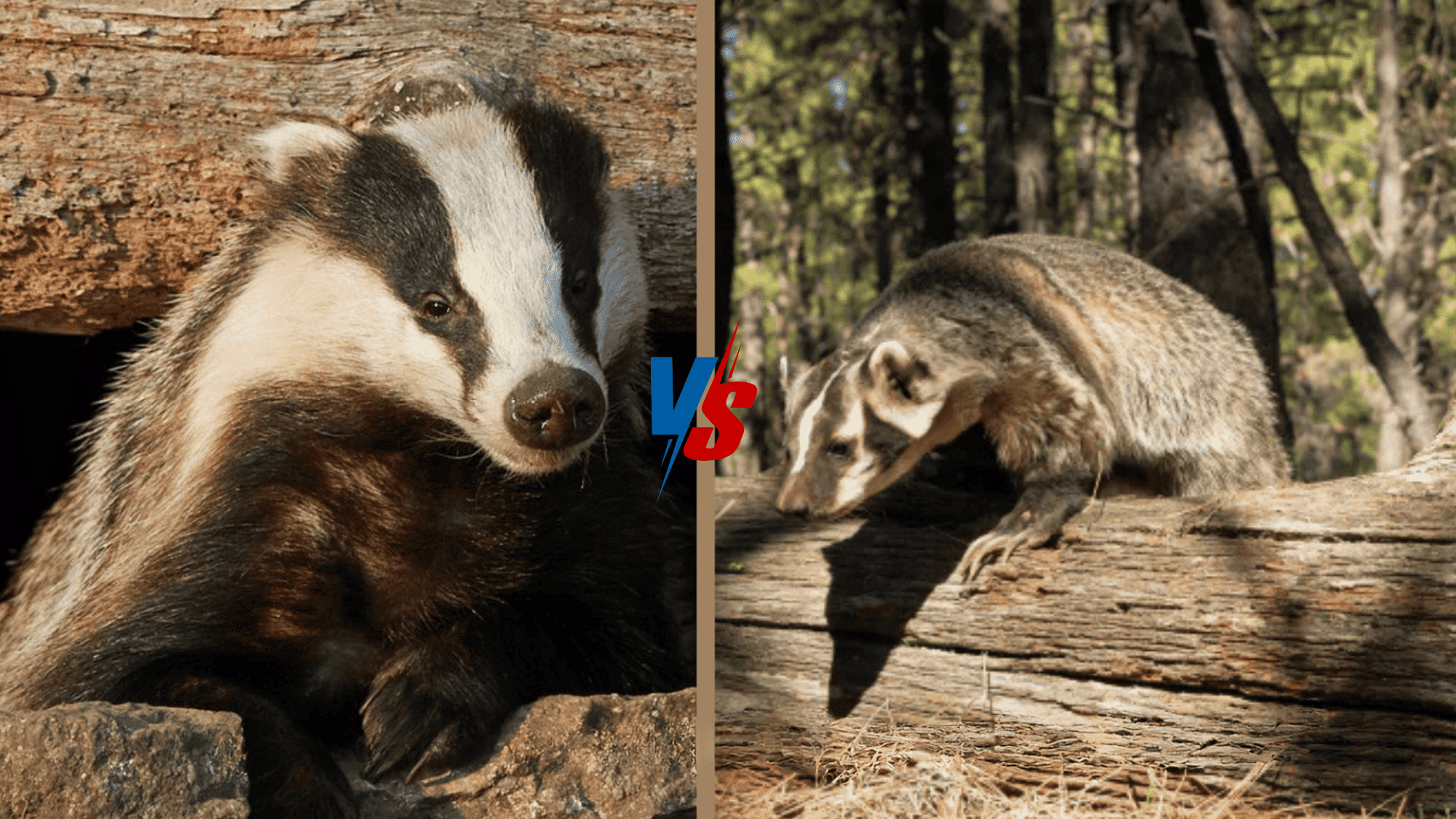
If you have ever seen a badger, you might have wondered if it’s an American or English badger.
Though they share some traits, these two badgers come from different parts of the world.
The American badger lives in North America, while the English badger is found in Europe.
They vary in size, diet, and social behaviors, making them interesting to compare.
In this blog, we will see the key differences and similarities between these two badgers.
By the end, you will understand what makes each one unique.
American Badger vs English Badger Comparison
| Feature | American Badger | English Badger |
|---|---|---|
| Life Expectancy | 9-10 years in the wild, up to 14 in captivity | 5-8 years in the wild, up to 15 in captivity |
| Social Behavior | Solitary, only social during mating season | Highly social, live in family groups or clans |
| Hunting Style | Mostly active at night, hunts small animals alone | Active at night, forages in groups, and relies on communal digging for food. |
| Dietary Preferences | Primarily carnivorous, feeds on insects, rodents, and small mammals | Omnivorous, feeds on earthworms, fruits, insects, and small mammals |
Meet the Species Classification and Groups
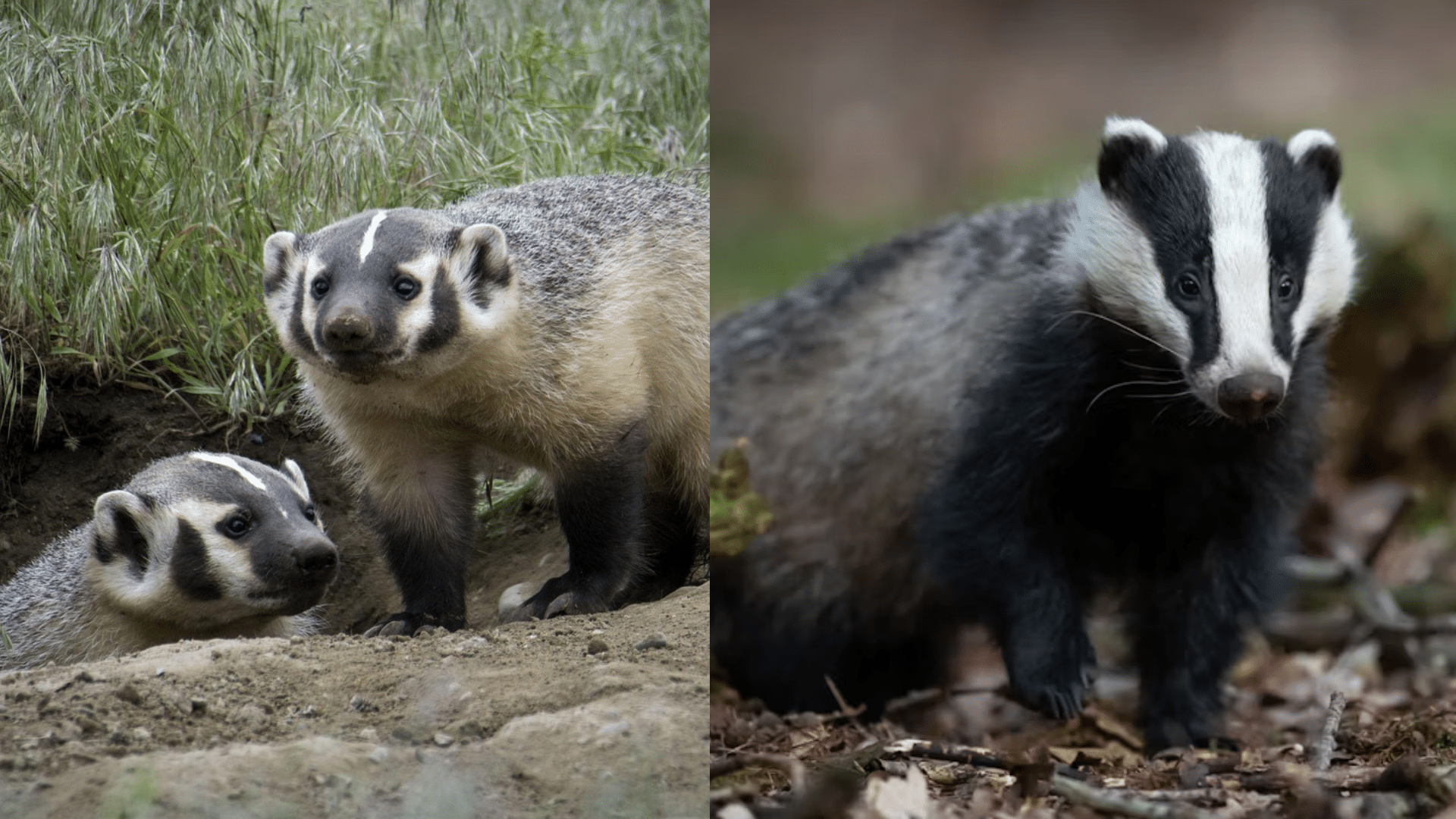

The American badger and English badger belong to the same Mustelidae family but have different classifications and subspecies, each adapted to their distinct environments across North America and Europe.
American Badger (Taxidea taxus)
The American badger, known scientifically as Taxidea taxus, is made up of four subspecies. Each one is found in different regions of North America. These subspecies are:
- Taxidea taxus taxus, which lives in the central USA and Canada.
- Taxidea taxus jacksoni, found in the Great Lakes region and Southern Ontario.
- Taxidea taxus jeffersoni, which is native to the Western USA and Alberta.
- Taxidea taxus berlandieri, located in Mexico and the Southwest USA.
English Badger (Meles meles)
The English badger, or Meles meles, also has four subspecies, but they are spread across Europe. These include:
- Meles meles meles, the most common subspecies, is found throughout Europe.
- Meles meles ibericus, which is native to Spain and Portugal.
- Meles meles kizlyarensis, found in parts of Russia and Eastern Europe.
- Meles meles norvegicus, which can be found in Norway and surrounding areas.
Evolution and Development
The American badger thrives in open prairies, while the English badger prefers wooded areas.
Both have developed similar traits, such as strong digging skills and nocturnal habits, connecting them within the Mustelidae family.
Physical Characteristics: Spotting the Differences
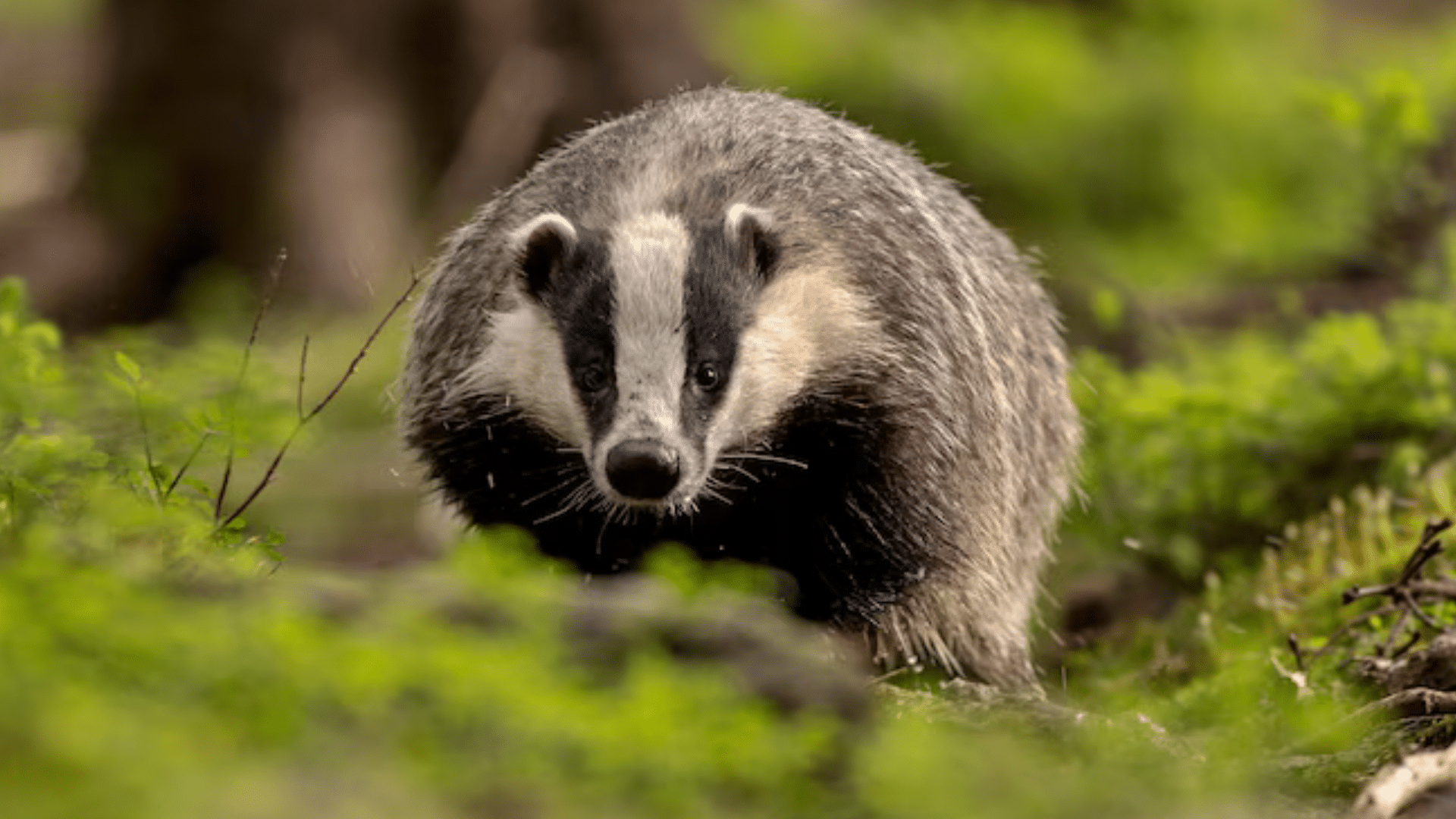

When it comes to telling the American badger and the English badger apart, you can look at their size, appearance, and facial features.
1. Size and Weight
- American Badger: These badgers are smaller, measuring about 20 to 30 inches long (excluding the tail) and weighing between 14 and 33 pounds.
- English Badger: The English badger is larger, ranging from 24 to 35 inches in length and weighing between 15 and 37 pounds. So, the English badger is usually bulkier.
2. Appearance
Fur Coloration:
- American Badger: Their fur is a mix of brown, gray, and white, with a rough texture. They also have noticeable black-and-white stripes on their face.
- English Badger: Their coat is mainly black and white with a smoother texture, giving them a sleeker look compared to the rougher American badger.
3. Distinctive Facial Markings
- American Badger: Their face has bold black-and-white stripes running from the nose to the neck, with some brown fur on the cheeks.
- English Badger: Their face has a neat black-and-white pattern that is smoother and more defined, with fewer markings around the cheeks.
4. Body Shape
- American Badger: They have a flatter body with shorter legs, which makes them compact and strong for digging.
- English Badger: English badgers are slightly stockier and more muscular, with short, powerful legs that aid them in digging.
5. Facial Features
The most noticeable difference is in the face. The American Badger has wider stripes, giving its face a rugged and bold appearance.
The English Badger has cleaner, sharper lines, making its face look more defined and symmetrical.
Habitat, Range, and Behavior
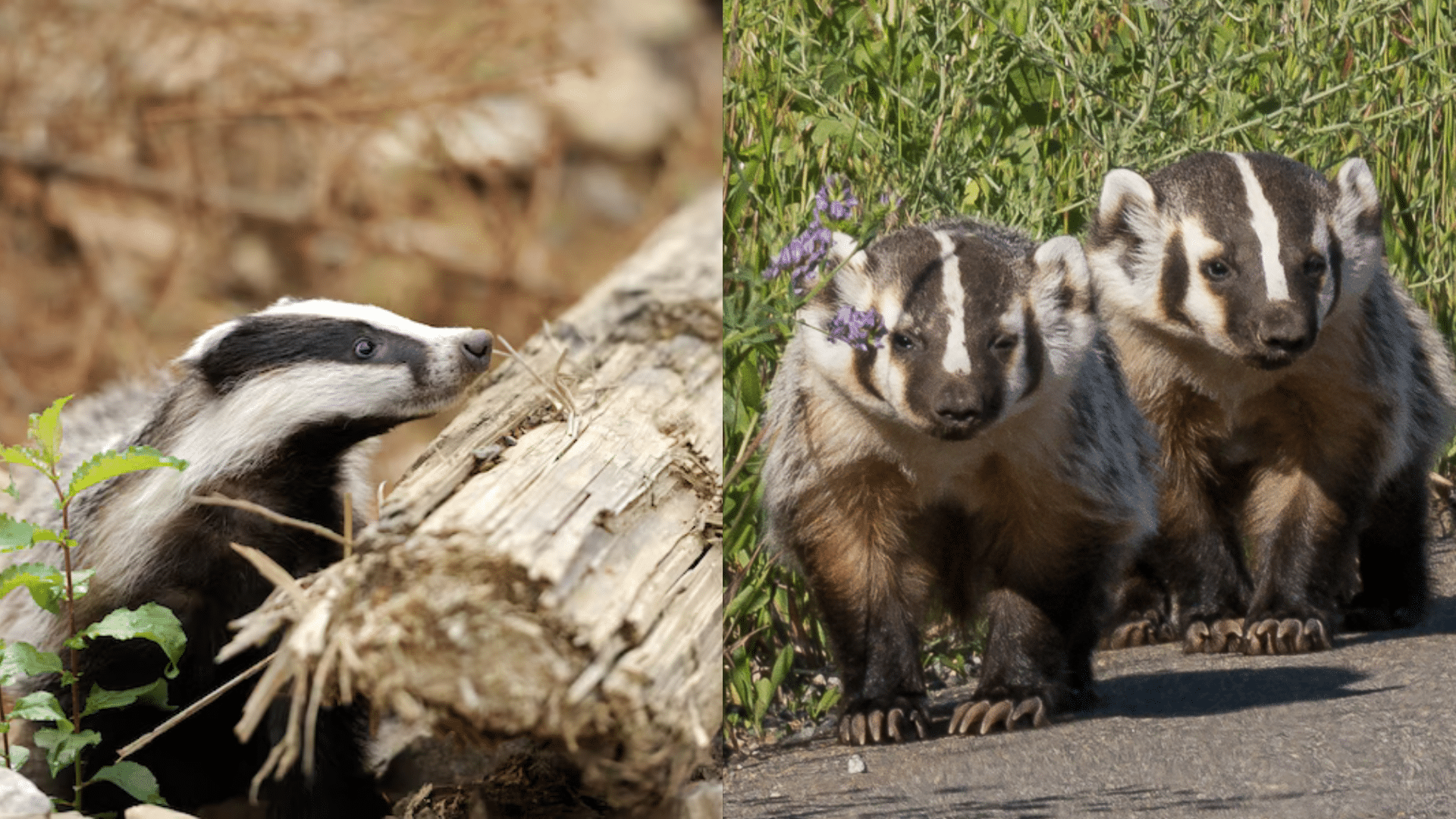

The American and English badgers have different habitats, ranges, and behaviors that help them thrive in their unique environments.
American Badger
- Habitat: Prefers open spaces, such as grasslands, prairies, and deserts.
- Range: Found across the USA, Canada, and parts of Mexico.
- Behavior: Solitary and mostly nocturnal. They dig deep burrows alone, sometimes sharing them with other animals, such as coyotes.
English Badger
- Habitat: Lives in woodlands, scrublands, and farmlands.
- Range: Found throughout Europe, especially in the UK.
- Behavior: Social and live in family groups or clans. They build complex burrow systems, called setts, with multiple entrances.
Diet and Foraging Habits: What’s on The Menu?
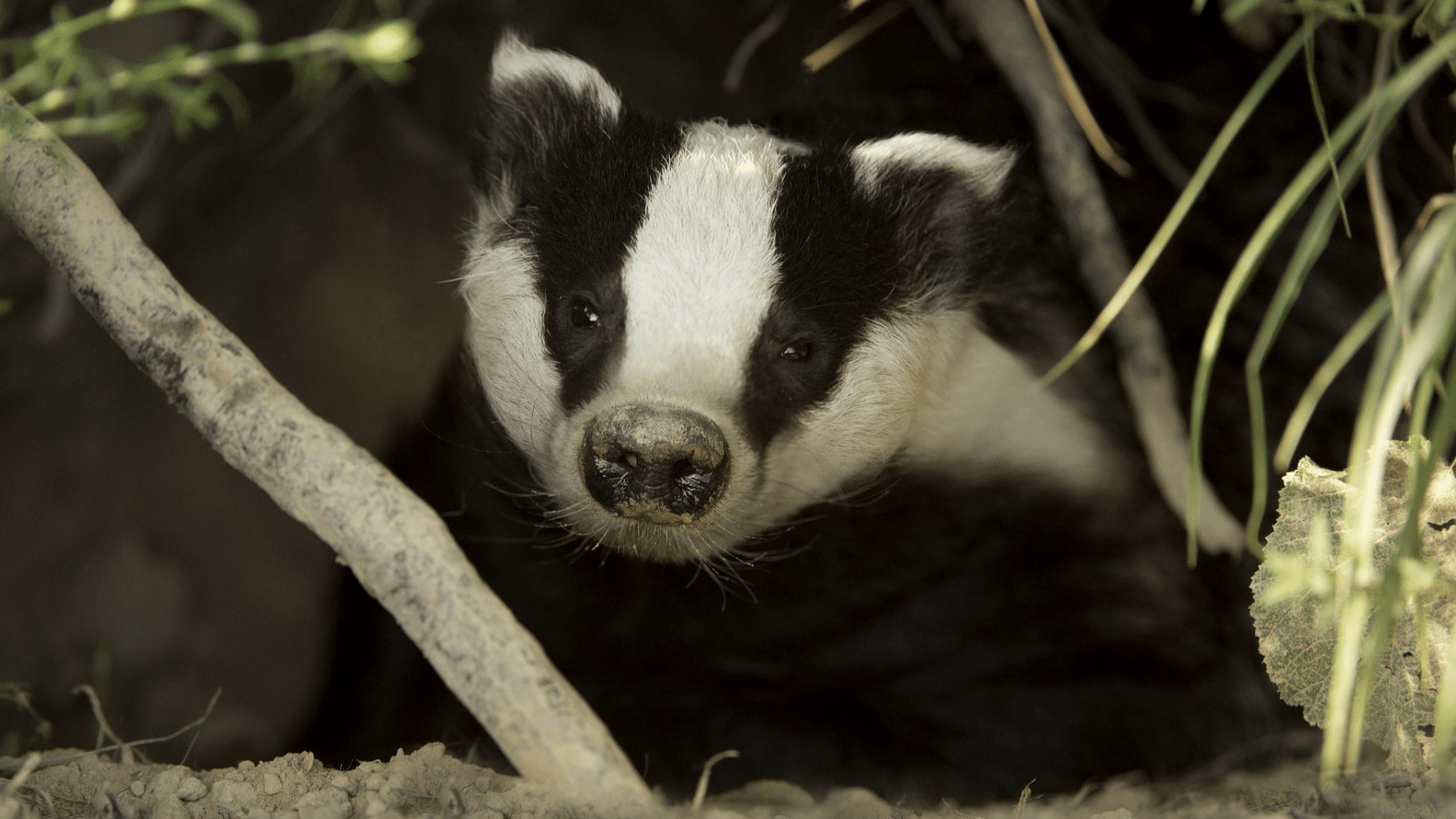

Let’s take a look at what the American and English badgers eat and how they find their food:
American Badger
The American badger is carnivorous, feasting on small prey like gophers, squirrels, moles, and insects. They use their sharp claws to dig out burrowing animals, making them skilled hunters.
They are known for their digging abilities, which they use to unearth prey like moles or rodents from the ground.
English Badger
The English badger is omnivorous, enjoying a variety of foods like earthworms, insects, fruits, grains, and even small mammals.
They tend to forage for whatever food is available in their environment.
These badgers forage at night, digging in the soil for worms and insects, but they also consume a wide range of plant material.
Both species have diets that match their habitats.
American badgers hunt smaller animals in open spaces, while English badgers have a more varied diet that reflects the diverse foods available in woodlands and farmlands.
Reproduction, Life Cycle, and Seasonal Behavior

Here’s an overview of how both badger species reproduce, their life cycle, and how their seasonal habits differ.
American Badger
- Reproductive Strategy: Mating occurs in late winter, followed by delayed implantation, allowing babies to be born in the spring. American badgers do not hibernate but are less active during the colder months.
- Seasonal Behavior: They remain active throughout the year, although they spend more time in their burrows during winter.
English Badger
- Reproductive Strategy: Similar to the American badger, they also have delayed implantation. However, English badgers tend to have larger litters and go into hibernation during the winter months.
- Seasonal Behavior: Hibernation is common during colder months, and they remain in their setts, only emerging when the weather warms up.
Both badgers adapt their behavior based on the seasons, with the American badger staying active year-round, while the English badger takes a break during the cold months.
Similarities Between American and English Badgers
| Feature | American Badger | English Badger |
|---|---|---|
| Family | Both species belong to the Mustelidae family. | Both species belong to the Mustelidae family. |
| Active at Night | Both are primarily active during the night. | Both are primarily active during the night. |
| Burrowing | Both are skilled diggers, creating burrows. | Both are skilled diggers, creating setts. |
| Strong Defense | Known for their fierce defense when threatened. | Known for their fierce defense when threatened. |
Conclusion
The American and English badgers are both remarkable creatures, each with unique traits that make them important in their ecosystems.
American badgers are solitary, carnivorous hunters, while English badgers are social, omnivorous foragers.
Both are skilled diggers.
Next time you encounter these badgers, take a moment to appreciate their adaptations and consider how we can help conserve their habitats.