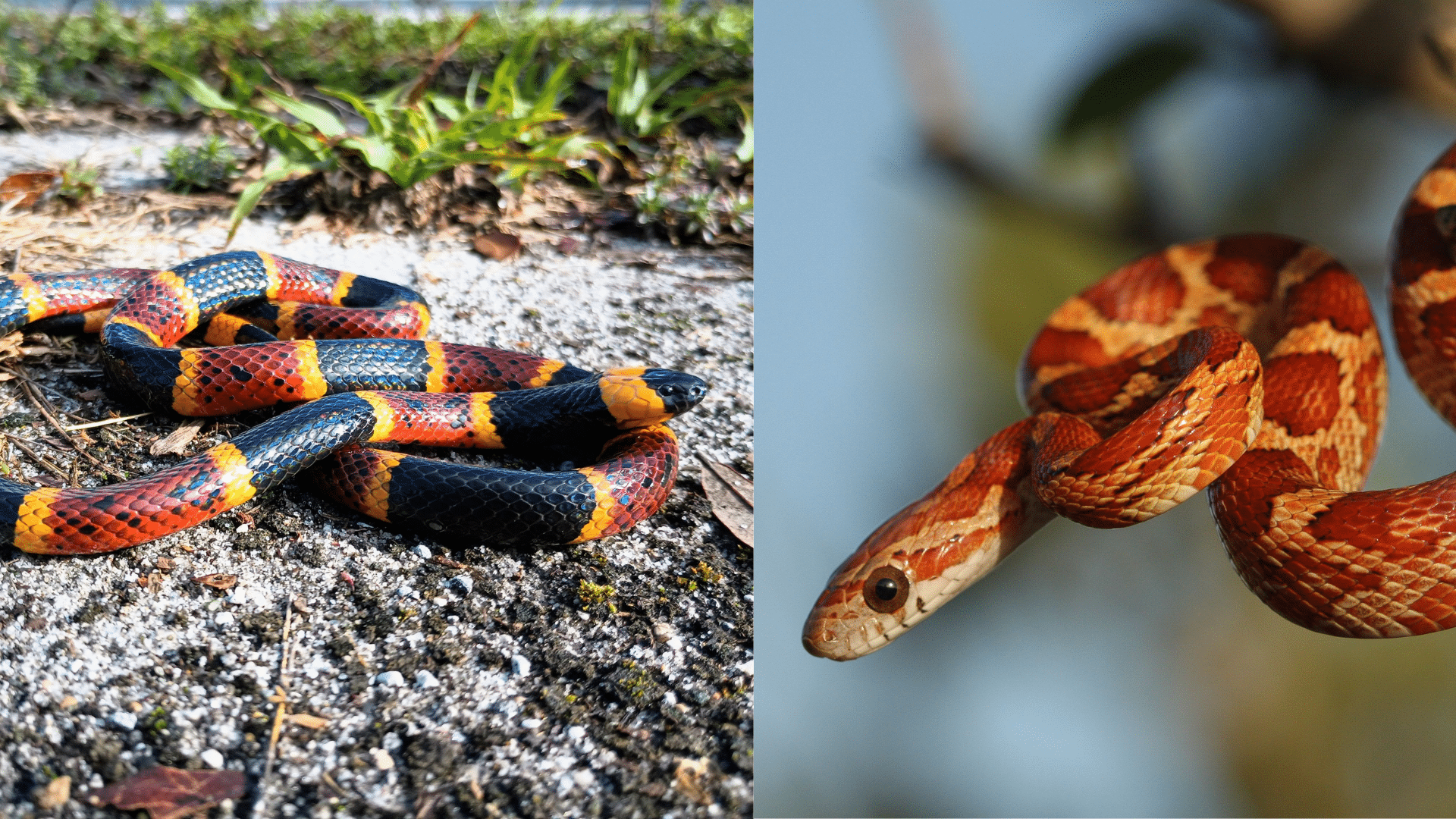
You are hiking and spot a colorful snake with red, black, and yellow bands.
Is this the deadly coral snake or the harmless corn snake? One bite from the wrong guess could ruin your day, while the other might just slither away peacefully.
These two snakes prove that looks can be seriously deceiving. Both sport eye-catching colors, but their personalities couldn’t be more different.
One’s a reclusive killer hiding underground, the other’s a gentle giant perfect for snake lovers.
Ready to learn the life-saving differences between nature’s most confusing look-alikes?
Comparison Between Coral & Corn Snake
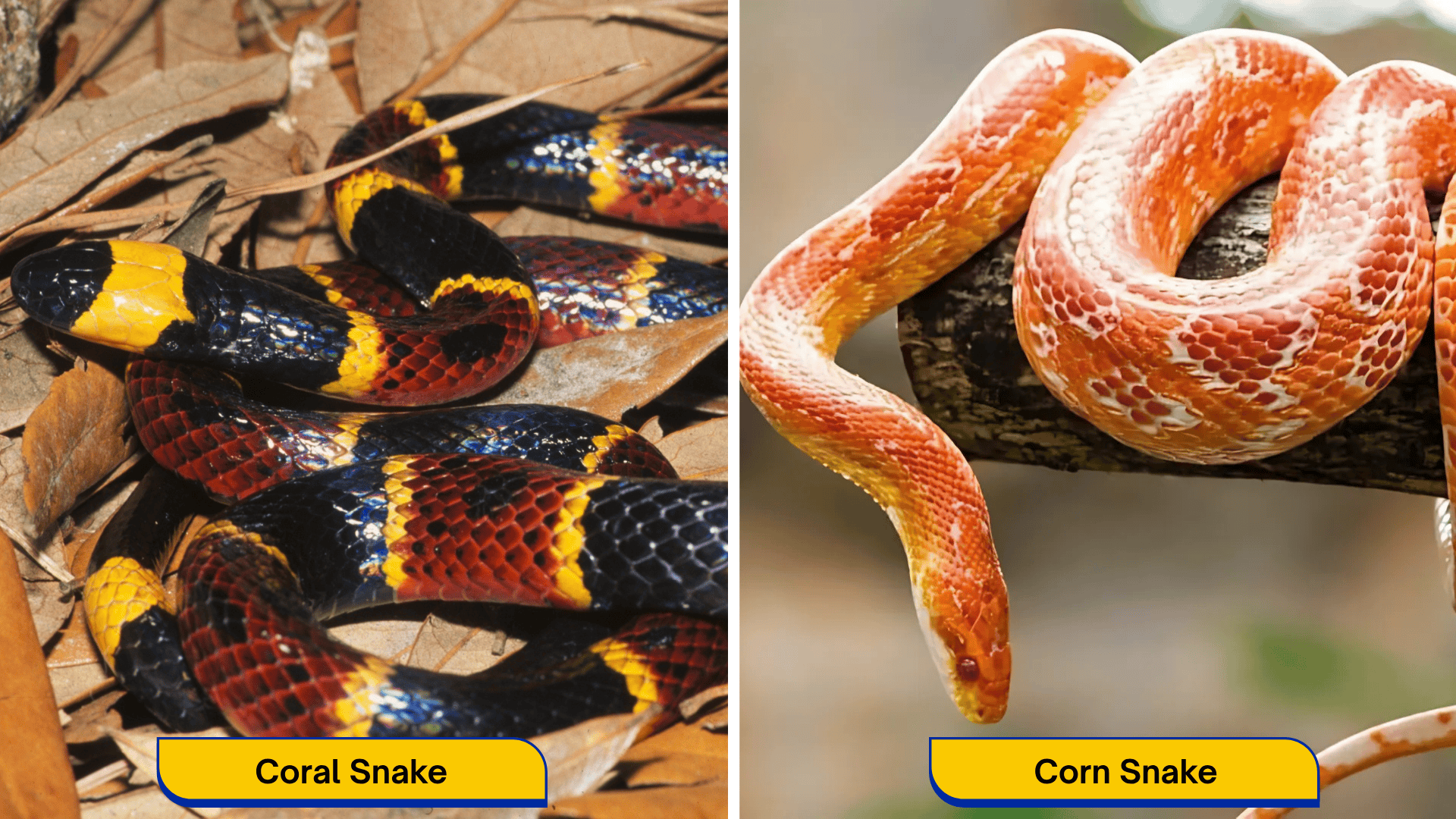

Snakes are diverse creatures, and the Coral Snake and Corn Snake stand out for their striking differences.
Let’s take a quick look at what makes each of these snakes unique, from their colors to their habitats and lifestyles.
1. Color Showdown: Stripes vs Subtle Tones
The vibrant appearance of these two snakes is one of the most noticeable differences.
Their colors and patterns play crucial roles in their survival in the wild.
- Coral Snake: Known for its vibrant, eye-catching red, yellow, and black stripes. This colorful pattern serves as a warning sign to predators, alerting them to the fact that the Coral Snake is venomous.
- Corn Snake: It has a more muted color palette, typically featuring orange, red, and brown, which helps it blend into its environment. Its pattern resembles that of corn kernels, making it perfect for hiding among leaf litter and branches.
Fun Fact: While the Coral Snake’s stripes scream “danger,” the Corn Snake’s patterns help it stay out of sight!
2. Venomous Traits: Danger vs Peace
The Coral Snake and Corn Snake are often confused, but their venomous abilities or lack thereof set them apart dramatically.
- Coral Snake: With its potent venom, the Coral Snake can pose a serious threat. Its venom attacks the nervous system, which can be dangerous, but bites are rare because of its shy nature.
- Corn Snake: Completely harmless, the Corn Snake is a non-venomous constrictor. It uses its strength to squeeze prey instead of relying on venom.
Fun Fact: While the Coral Snake’s venomous bite can be deadly, it’s much more likely to avoid humans than strike!
3. The Gentle Giant: Calm and Collected
Personality differences distinguish the Corn Snake and the Coral Snake in their behavior around humans and other animals.
- Corn Snake: These snakes are incredibly friendly and popular for their calm demeanor, making them an ideal pet. They rarely bite and enjoy being handled by humans, which makes them popular in the pet trade.
- Coral Snake: In contrast, Coral Snakes are reclusive and prefer to stay hidden in their environments. If threatened, they’re more likely to retreat than to engage.
Fun Fact: Corn Snakes are often referred to as “gentle giants” because of their peaceful nature, despite their long, slender bodies!
4. Habitat Wars: Where They Thrive
Each snake has a specific environment that suits its needs, showcasing how they’re adapted to different ways of life.
- Coral Snake: Prefers tropical and subtropical habitats like forests, grasslands, and underbrush where it can easily hide. They’re often found in the southern U.S., Mexico, and parts of Central America.
- Corn Snake: More adaptable, Corn Snakes survive in a range of environments, from forests and grasslands to farmlands and barns. They are found throughout the eastern U.S.
Fun Fact: While Coral Snakes seek shelter in warm, humid climates, Corn Snakes can be found from farms to homes, thanks to their adaptability!
5. Encounters in The Wild: Defense Mechanisms
When these snakes encounter threats, their responses differ significantly, reflecting their innate instincts.
- Coral Snake: When threatened, the Coral Snake often retreats into its burrow or hides in the underbrush. It rarely confronts predators, preferring to avoid danger rather than engage in a fight.
- Corn Snake: Corn Snakes also rely on avoiding danger, but will defend themselves by coiling and hissing if they feel cornered. If provoked, they may strike but are unlikely to bite without cause.
Fun Fact: The Coral Snake’s first defense is to flee, whereas the Corn Snake’s first line of defense is a good hiss and a threat display!
6. Hunting Style: Striking vs Constricting
The way each snake hunts is closely tied to its physical abilities and the environment in which it lives.
- Coral Snake: The Coral Snake is a solitary hunter, feeding mainly on small reptiles and amphibians. It strikes quickly with its venom to immobilize prey, then swallows it whole.
- Corn Snake: Known as a constrictor, the Corn Snake hunts small mammals, birds, and eggs. It strikes its prey, wraps around it, and squeezes until it suffocates.
Fun Fact: The Coral Snake’s venom allows it to catch prey quickly, while the Corn Snake’s constriction method lets it hunt a variety of animals!
7. Life Span: Who Stays Around Longer
- Coral Snake: In the wild, Coral Snakes live around 6 to 8 years, but their lifespan is typically shorter in captivity due to specialized care needs.
- Corn Snake: Corn Snakes have a significantly longer life expectancy, living up to 10 years in the wild, and up to 20 years in captivity with proper care.
Fun Fact: If you want a long-term snake companion, the Corn Snake is your best bet, as it can easily outlive its venomous cousin.
Wrapping It Up
Two snakes, wildly different personalities, yet both perfectly designed for their worlds.
The coral snake commands respect with its lethal bite, while the corn snake wins over hearts as the perfect companion.
Every creature has its purpose, whether it’s controlling rodent populations or reminding us to stay alert in the wild.
So, take a moment to learn its story today!