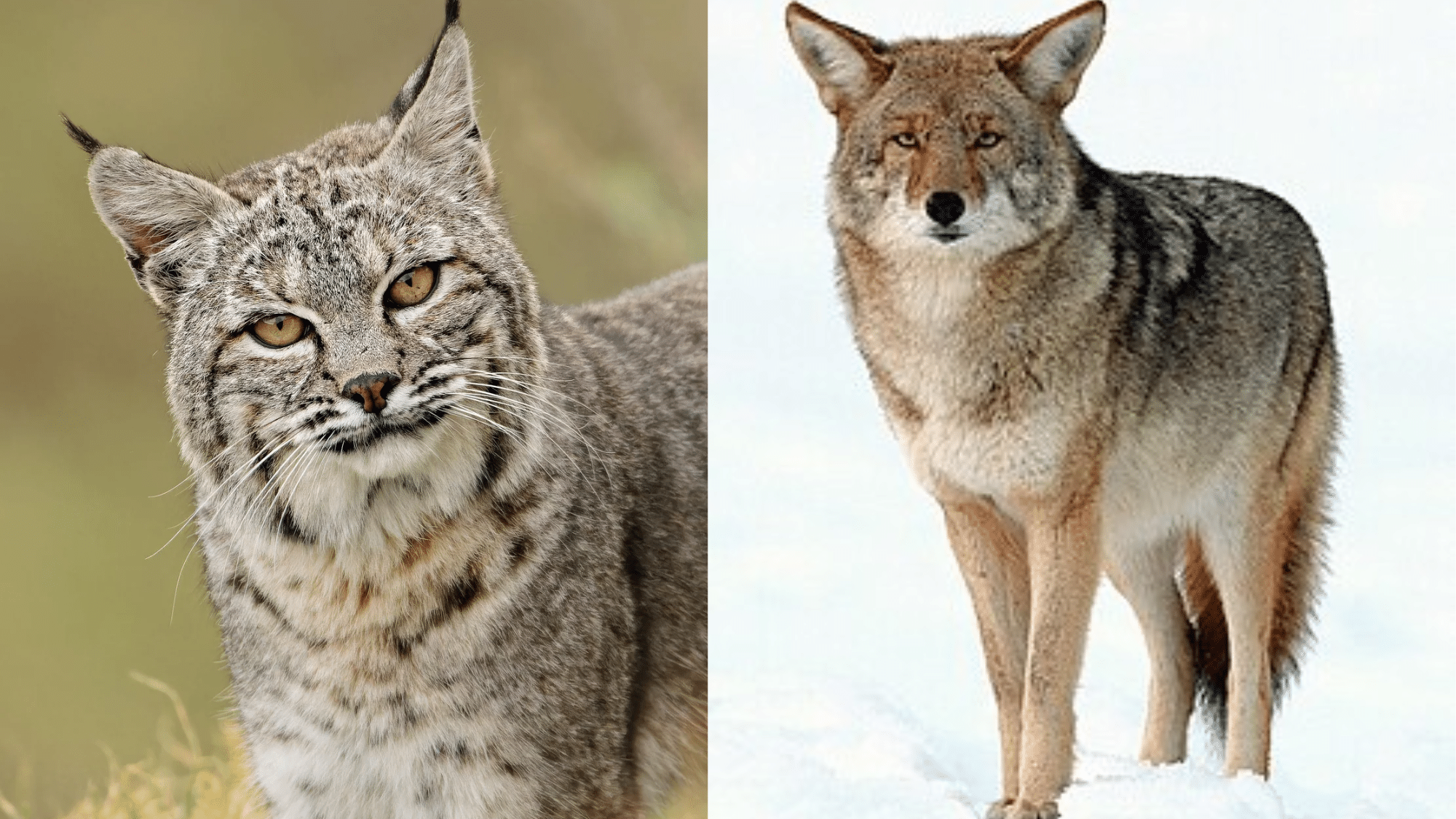
Have you ever spotted a wild animal and wondered if it was a bobcat or a coyote?
These two North American predators might share the same territories, but they look and behave quite differently.
However, knowing what sets them apart, from their size and appearance to their hunting habits, can help you identify which animal you have encountered.
Ready to learn how to identify these creatures?
Let’s begin!
1. Physical Appearance and Size
| Feature | Bobcat | Coyote |
|---|---|---|
| Body Shape | Stocky, cat-like | Lean, dog-like |
| Size | 15-35 lbs, 2-3 feet long | 20-50 lbs, 3-4 feet long |
| Tail | Short, bobbed tail (4-7 inches) | Long, bushy tail (12-16 inches) |
| Coat | Spotted coat, often reddish-brown or grayish | Solid colored, typically grayish-brown or yellowish-gray |
| Ears | Tufted ears with black markings | Pointed ears without tufts |
| Face | Short snout, whiskers, cat-like face | Long snout, dog-like face |
2. Habit and Behaviour
Bobcats and coyotes differ in how they behave in the wild, especially in terms of hunting, territory, and social structure.
Bobcats
- Solitary hunters.
- Mark their territory using scent.
- Active mostly at night (nocturnal).
- Prefer dense forests or rocky areas.
Coyotes
- Often travel in packs or family groups.
- Can be diurnal (active during the day) or nocturnal.
- Highly adaptable, found in a wide range of habitats.
- Known for their distinctive howls used for communication.
3. Dietary Habits
Bobcats are strict carnivores that primarily hunt rabbits, rodents, birds, and occasionally small deer. Their diet consists almost exclusively of meat, which they obtain through stalking and ambush hunting.
Whereas, coyotes are opportunistic omnivores with a varied diet. They eat small mammals, fruits, berries, insects, and carrion. Their adaptable habits allow them to survive in diverse environments.
4. Hunting Techniques and Speed
Bobcats hunt alone, using stealth and quick bursts of speed. They sneak up on prey and pounce suddenly.
- Speed: Up to 30 mph
- Style: Ambush hunting in forests or rocky areas
And, the Coyotes are flexible hunters. They may hunt alone or in small groups, chasing prey over longer distances.
- Speed: Up to 40 mph
- Style: Endurance chasers in open areas like grasslands
5. Bite Force & Fighting Style
Bobcats have powerful jaws and sharp claws. They rely on surprise attacks, using their strength and agility to take down prey with a quick, deadly strike.
But the coyotes use their bite and stamina during fights. They often chase and wear down prey, relying on endurance rather than strength. When hunting in groups, they work together to bring down larger animals.
Note: While bobcats have a stronger bite for their size, coyotes depend more on repeated bites and persistence.
6. Seasonal Adaptations
Bobcats maintain relatively consistent hunting patterns year-round, though they may target different prey based on availability. During winter, they might focus more on larger prey to maximize caloric intake.
In the case of coyotes, they dramatically shift their diet with the seasons. In summer and fall, they consume more fruits and vegetables. During winter, they rely more heavily on meat.
Who Would Win in a Fight
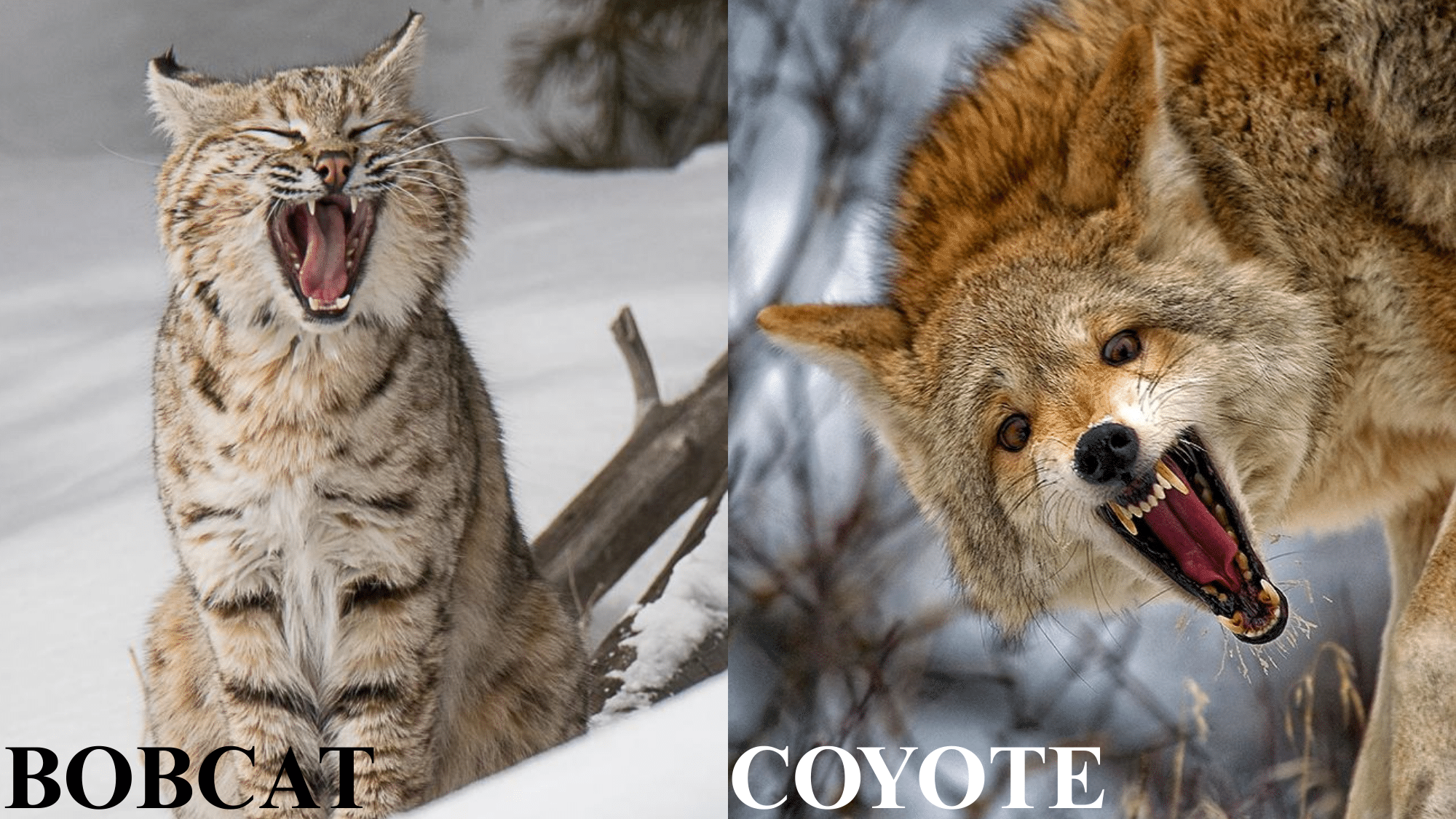

In a one-on-one encounter, the coyote might have the upper hand due to its larger size and stamina. However, a bobcat’s sharp claws and ambush skills could turn the tide if it strikes first.
- Coyote: Bigger, more durable, and aggressive in longer fights
- Bobcat: Smaller but agile, with powerful claws and a strong bite
Verdict: The coyote likely wins in most cases, but a bobcat could still take the lead with the right timing and surprise.
Some Interesting Facts About Bobcat and Coyote
These facts highlight the unique adaptations and characteristics that make bobcats and coyotes successful predators in their respective ecological niches.
Bobcat Facts
- Bobcats can jump up to 12 feet in a single bound.
- They have night vision six times better than humans.
- Female bobcats raise their young alone without male assistance.
- Their pawprints lack claw marks due to retractable claws
- Bobcats are the most common wildcat in North America
- Their territories typically range from 5-50 square miles
Coyote Facts
- Coyote pairs often mate for life.
- They’ve expanded their range by nearly 40% since the 1950s.
- Their population often increases when hunted due to complex reproductive responses.
- They can digest foods ranging from meat to fruits to garbage.
- Coyotes now live in major cities including Chicago, New York, and Los Angeles.
Wrapping It Up
Now that you know the key differences between bobcats and coyotes, spotting these wild neighbors would be much easier!
From the bobcat’s spotted coat and bobbed tail to the coyote’s dog-like appearance and varied diet, each animal has adapted perfectly to its role in nature.
In short, this guide helps you confidently tell whether you have spotted a bobcat or a coyote.