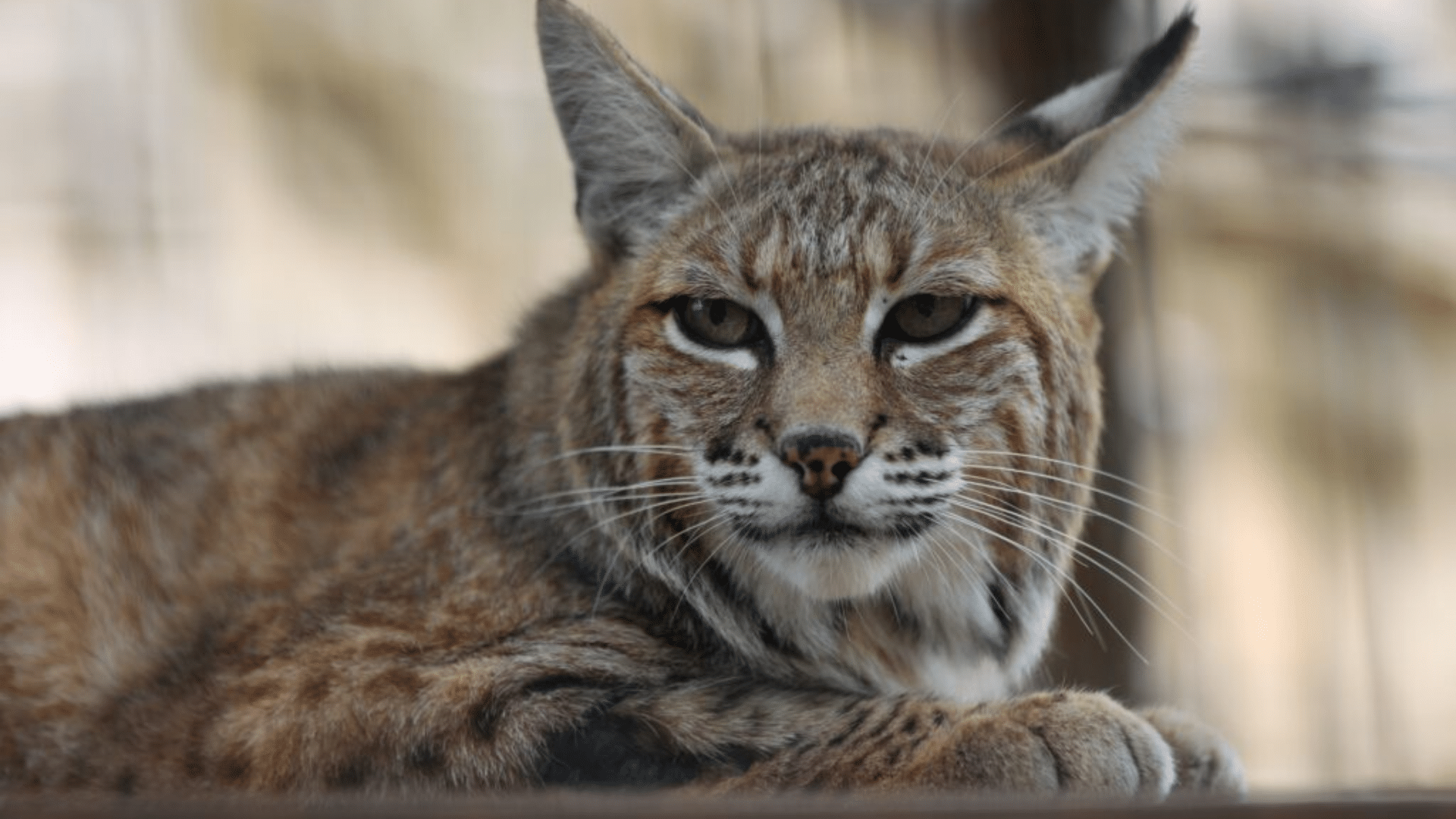
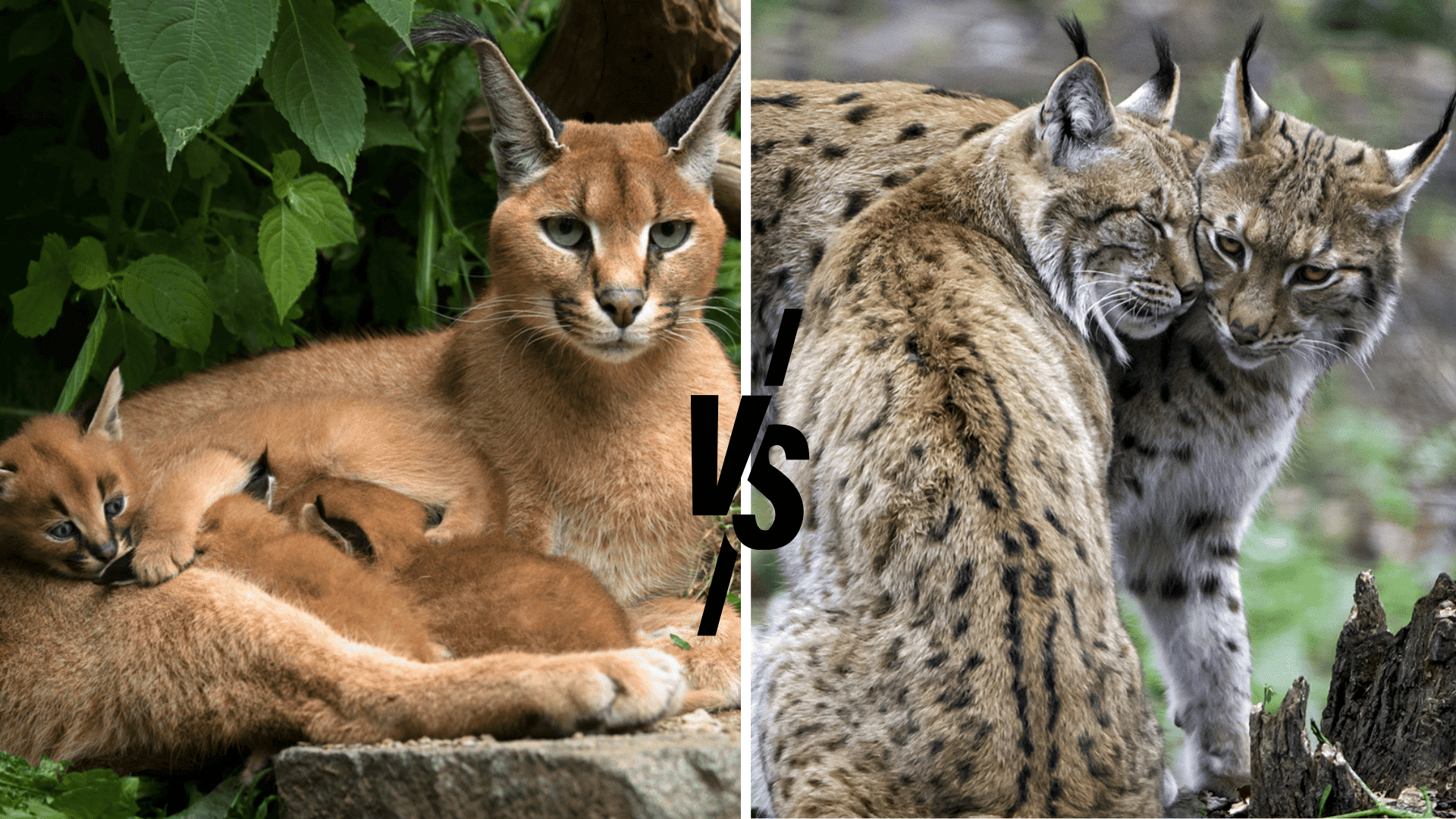
Caracals and lynxes might look like long-lost cousins with their pointed ear tufts and stealthy moves, but these wild cats couldn’t be more different. One rules the hot, dry deserts while the other owns the snowy forests.
Think about it: caracals can leap incredibly high to snatch birds right out of the air, while lynxes use their oversized paws like natural snowshoes to hunt silently through winter landscapes. Both cats have mastered completely different worlds.
Let’s explore what makes these ear-tufted hunters so unique and why those fancy ear decorations are actually survival tools in disguise.
Taxonomy & Classification
Despite their similar appearance, caracals and lynxes belong to completely different branches of the cat family tree.
Here’s how these ear-tufted hunters are actually classified in the scientific world.
| ASPECT | CARACAL | LYNX |
|---|---|---|
| Scientific Classification | Separate genus Caracal caracal | Four species in genus Lynx (L. lynx, L. canadensis, etc.) |
| Common Misconception | Often called “desert lynx” but genetically distinct | True lynx species with shared evolutionary lineage |
| Family Relationship | Felidae family member but not a true lynx | Genuine lynx genus within Felidae family |
| Geographic Distribution | Desert and arid regions | Snowy forest ranges in Eurasia and North America |
While both cats share the Felidae family, their evolutionary paths diverged long ago. The caracal earned its “desert lynx” nickname purely from appearance, but science tells a different story about these remarkable felines.
Traits That Separate Caracal and Lynx
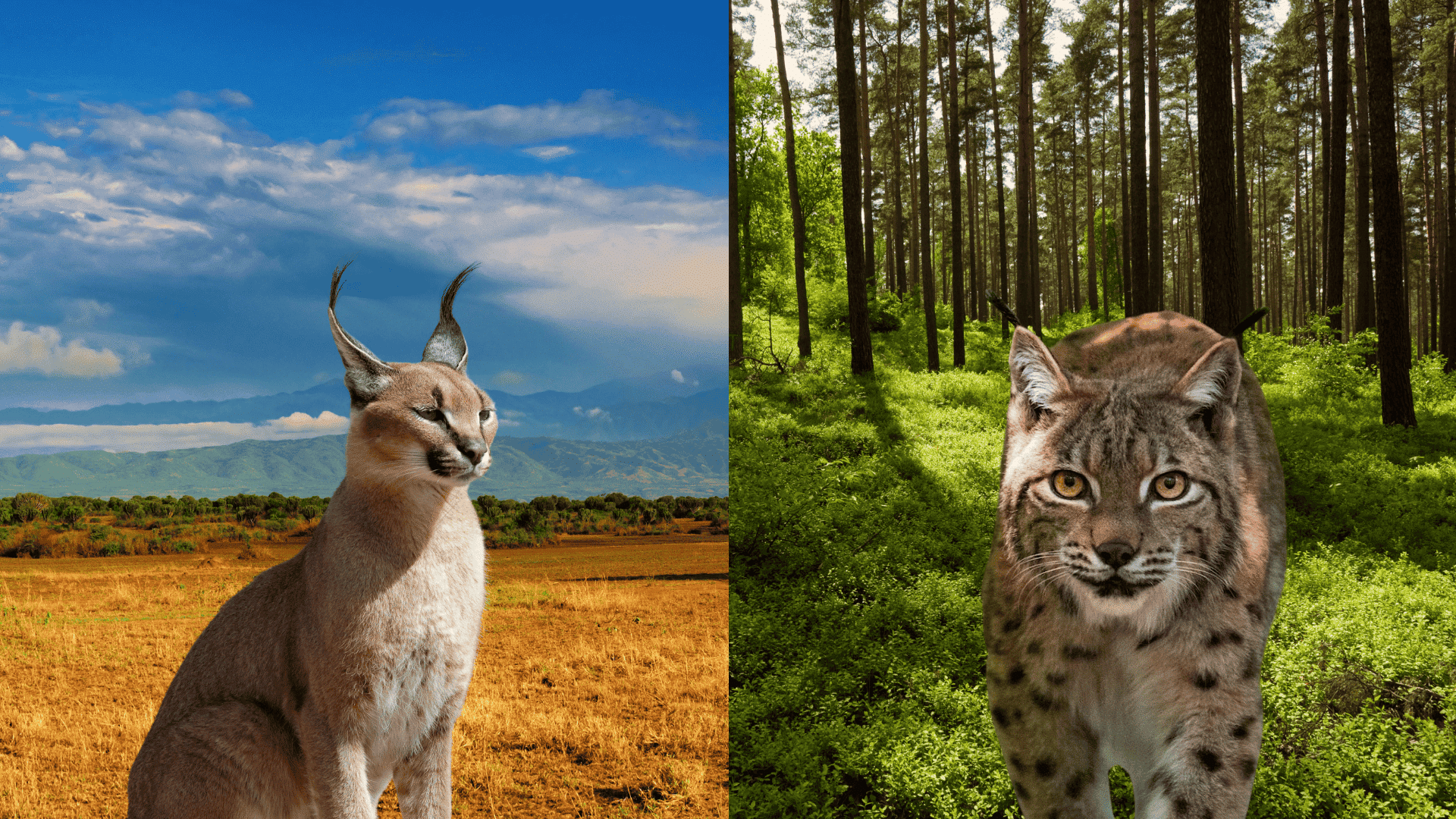
These distinctive felines share similarities, but their unique characteristics set them apart in fascinating ways.
1. Body Structure
| FEATURE | CARACAL | LYNX |
|---|---|---|
| Body Size | Sleek, slender, athletic | Stockier, more robust |
| Appearance | Long-legged, graceful | Shorter legs, compact build |
| Build | Built for speed and agility | Built for strength, power |
2. Ear and Facial Features
These cats’ distinctive faces help wildlife observers identify them at a glance.
- Caracal: Long, black ear tufts, small face, pronounced cheekbones.
- Lynx: Ear tufts (usually shorter), broad face with prominent ruff/beard.
3. Coat and Coloration
Their fur patterns reflect adaptations to their native environments.
- Caracal: Uniform reddish-tan or golden coat, minimal markings.
- Lynx: Spotted or mottled fur, often grayish or brown, with a short tail tipped in black.
4. Tail
The tail structure provides another clear visual distinction between these wild cats.
- Caracal: Longer, slender tail with a black tip.
- Lynx: Short, stubby tail, always with a distinct black tip.
5. Hunting and Diet Comparison
Both caracals and lynxes are skilled predators, but they’ve developed completely different hunting strategies based on their environments. One soars through the air to catch prey, while the other perfects the art of patient ambush.
| FEATURE | CARACAL | LYNX |
|---|---|---|
| Hunting Style | Stealthy stalk and pounce | Ambush predator waits in cover |
| Approach | Leaps high to catch birds | Prefers ground prey, uses cover |
| Preferred Prey | Birds, small mammals, and rodents | Hares, rabbits, rodents, birds |
| Feeding Frequency | Opportunistic, daily | Opportunistic, daily |
| Hunting Location | Open savannas, scrublands | Forests, woodlands, tundra |
These hunting differences show how each cat has perfectly adapted to its habitat. The caracal’s aerial acrobatics work beautifully in open landscapes, while the lynx’s patient ambush style dominates in dense forest cover where stealth is everything.
6. Habitat Preferences
The natural ranges of these cats rarely overlap due to their distinct habitat requirements.
Caracal
Dry savannas, semi-deserts, scrublands of Africa, and parts of the Middle East and India. Prefers open terrain with sparse cover.
Lynx
Boreal forests, temperate woodlands, and snowy regions of Europe, Asia, and North America (species-dependent: Eurasian lynx, Canada lynx, Iberian lynx, Bobcat). Prefers dense forests, rocky outcrops, and areas with thick undergrowth.
Traits that Make Them Similar
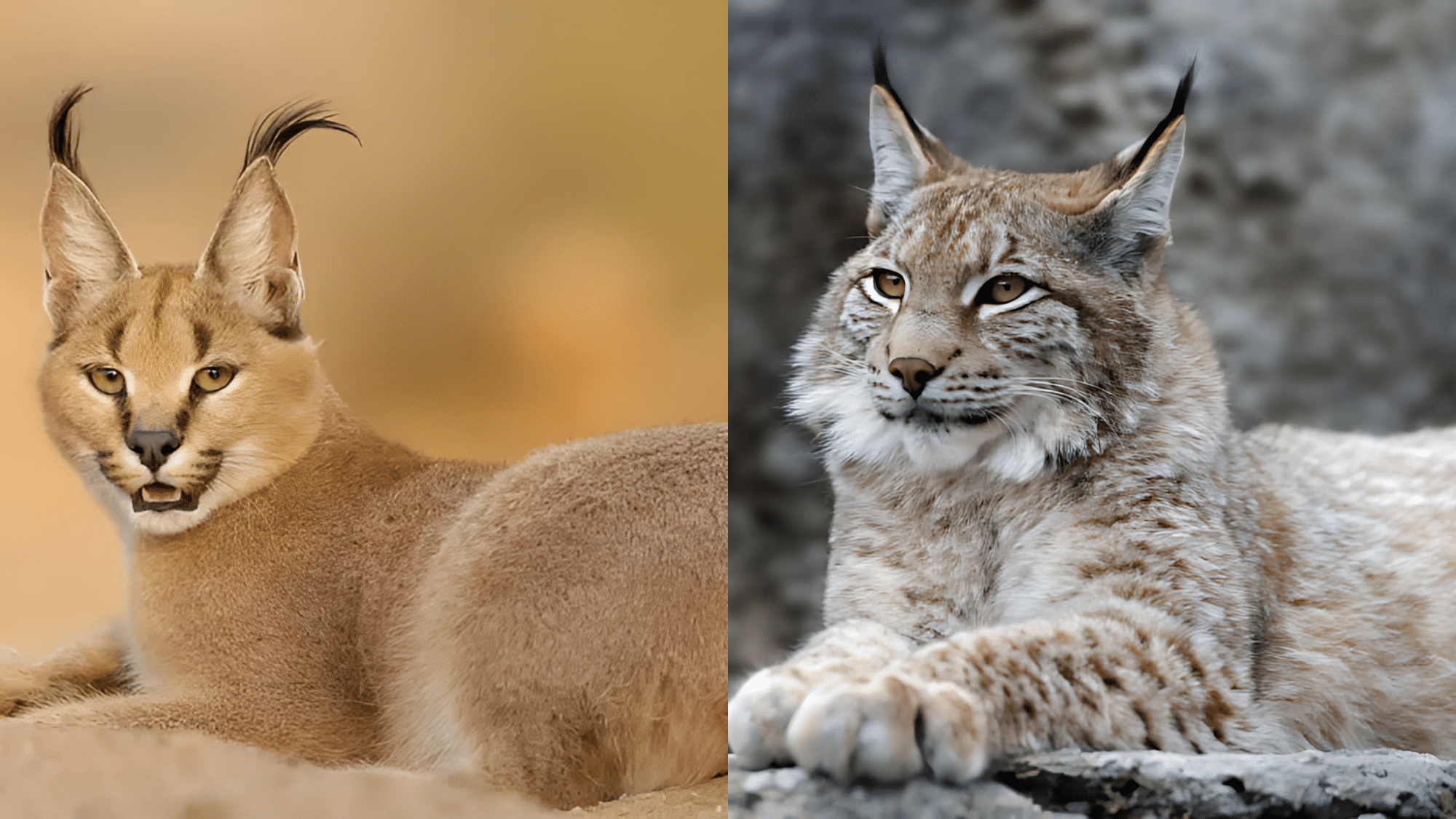
Despite their differences, these felines share common adaptations that mark them as skilled predators.
Physical Similarities
Both cats possess physical traits that make them effective hunters in their respective habitats.
-
Similar Body Structure: Both have agile, powerful builds that allow for quick movements and stealthy approaches when hunting.
-
Sharp Claws and Teeth: Their claws and teeth are designed for grasping and killing prey, making them formidable predators.
-
Camouflage Abilities: Both animals have coat colors or patterns that help them blend into their surroundings, aiding in their stealth during hunts.
-
Strong, Flexible Bodies: Their bodies are designed for quick pounces or bursts of speed, helping them close the gap between themselves and their prey efficiently.
Behavioral Similarities
These wild cats exhibit comparable behaviors despite living in different parts of the world.
-
Solitary and Territorial: Both animals prefer to live alone and defend their territory from others, ensuring they have ample resources for themselves.
-
Exceptional Hearing and Vision: Their keen senses allow them to detect prey and threats from great distances, making them efficient hunters and survivors.
-
Stealth and Ambush Tactics: Both use the element of surprise to catch prey, silently approaching before launching a sudden attack.
-
Crepuscular/Nocturnal Hunters: These animals are most active during dawn, dusk, or night, when they can avoid predators and hunt more effectively in low light.
Interesting and Fun Facts About Caracal and Lynx
These remarkable cats possess surprising abilities that highlight their specialized evolution.
Caracal Facts
These agile hunters have adapted perfectly to their arid environment.
- Caracals can jump up to 3 meters (10 feet) in the air, allowing them to catch birds mid-flight with their sharp claws.
- Their name comes from the Turkish word karakulak, which means black ear, referring to the distinctive black tufts on their ear tips.
- Despite their medium size, caracals are remarkably strong and can bring down prey three times their weight, including small antelopes.
- Caracals need very little water to survive and get most of their moisture from the bodies of their prey, making them well-suited for arid environments.
Lynx Facts
These northern cats have specialized adaptations for life in cold, snowy regions.
- The lynx has enormous paws that act like natural snowshoes, spreading their weight across snow and allowing them to move quickly in winter conditions.
- A lynx’s hearing is so sharp that it can detect a mouse under more than a foot of snow.
- The tufts on a lynx’s ears may work as hearing enhancers, similar to radar dishes, helping them locate prey with amazing accuracy.
- Unlike many cats, lynxes are not territorial about their hunting grounds and will often share large areas with other lynxes, though they hunt alone.
These incredible adaptations show how evolution has shaped each species to thrive in completely different worlds: one mastering the art of desert survival, the other conquering the challenges of snowy wilderness.
That’s a Wrap
After exploring these remarkable cats, it’s clear that nature has no shortage of creative solutions. The caracal’s desert acrobatics and the lynx’s snow-silent hunting prove there’s more than one way to be a successful predator.
What’s really striking is how perfectly each cat fits its world, from the caracal’s water-efficient body to the lynx’s oversized snowshoe paws. Every feature tells a story of thousands of years of fine-tuning.
These cats remind us that survival isn’t about being biggest or strongest, but becoming exactly what your environment needs you to be.