Space holds countless wonders that make us look up in awe. Our night sky contains stars, planets, and galaxies full of secrets waiting to be found.
When you gaze at the stars, you join a human tradition that goes back thousands of years.
People have always watched the skies to learn about our place among the stars.
This list of astronomy facts will show you things you might not know about our solar system and beyond.
Amazing Facts About Astronomy
From our nearby planets to distant stars, the universe tells an ongoing story billions of years in the making.
Let’s examine some interesting space facts together.
1. Sun Size Shocker
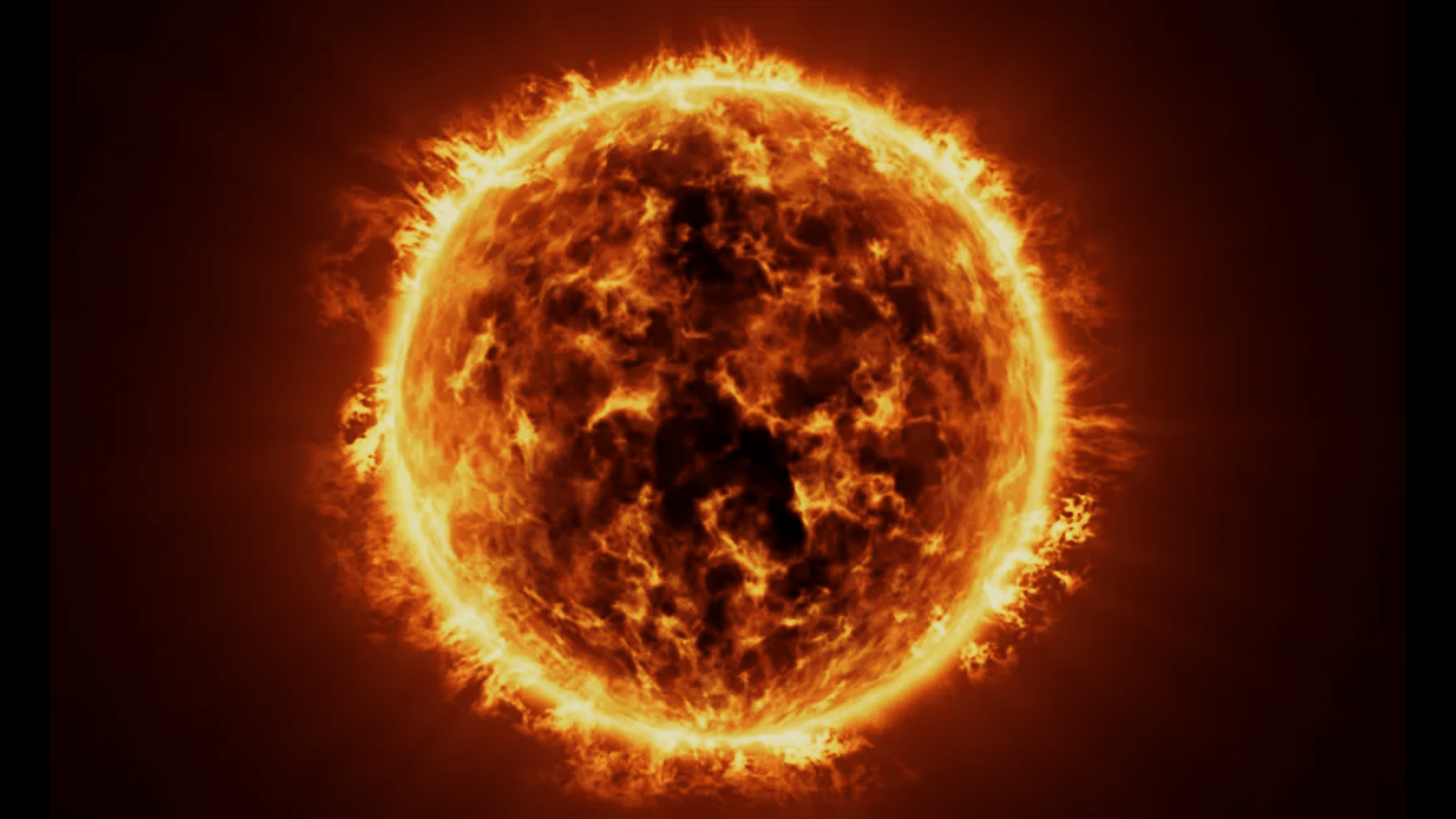

Did you know? The Sun makes up 99.86% of all mass in our solar system.
You could fit about 1.3 million Earths inside the Sun! That’s like trying to fill a basketball with grains of sand.
When looking up at the sky, many people are struck by how small the Sun appears from Earth.
Yet this humble-looking dot holds tremendous power and size. It’s a good reminder that things in space aren’t always what they seem.
2. The Two-Month Monday
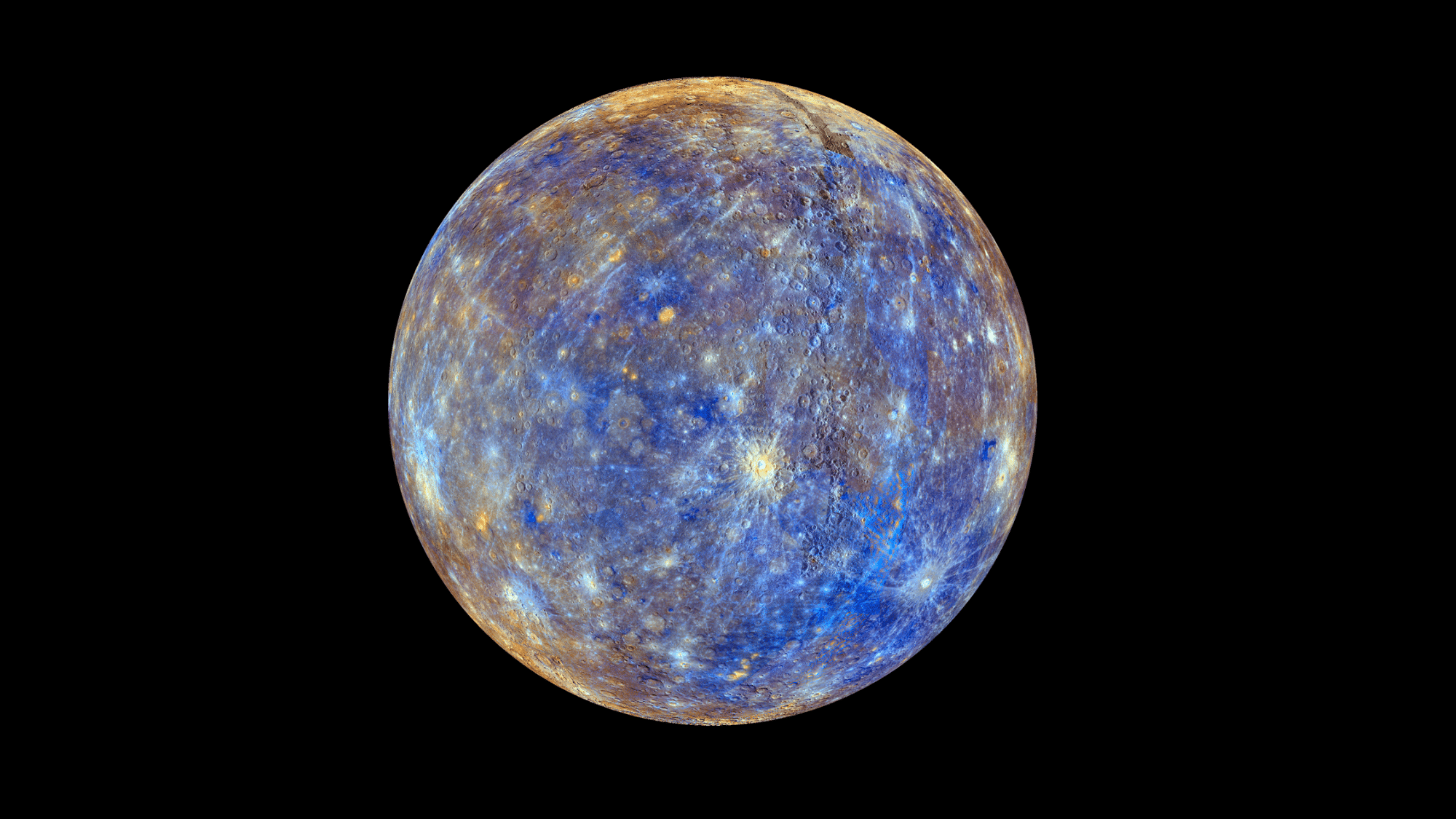
Fun Fact: On Mercury, weekends are rare
- One day lasts 59 Earth days
- One year is only 88 Earth days
- A single day takes up 2/3 of the year!
If you lived on Mercury, you would only see about 1.5 days per year. Your Monday morning would last weeks, and your weekend would be over before you knew it.
School kids on Mercury would have a very strange schedule class might last for a month of Earth time.
3. Backwards Sunrise World
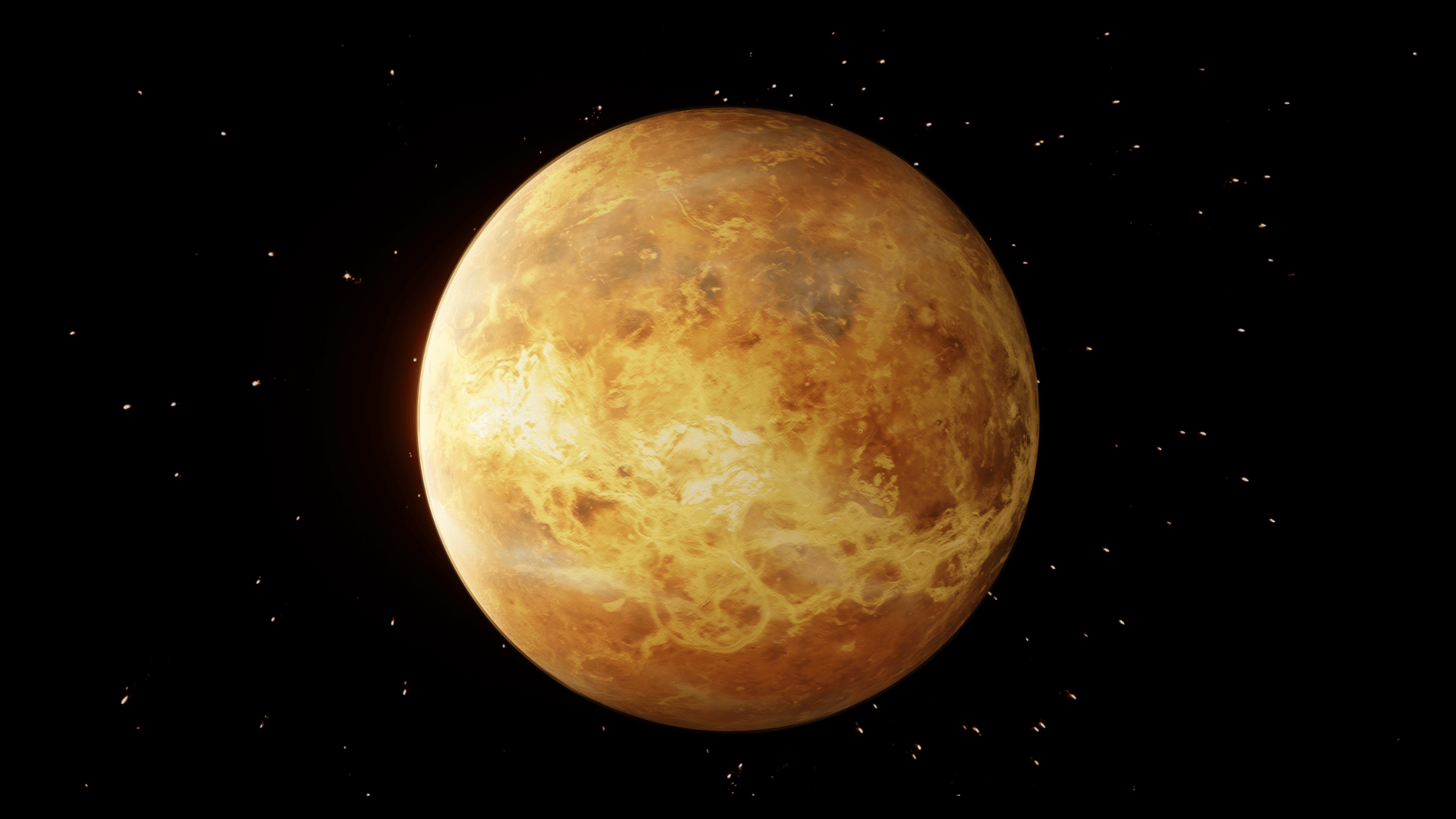
Venus: The Planet Where East and West Switched Places
Most planets in our system spin one way, but Venus does the exact opposite. On Venus, you would watch the Sun climb up from the western horizon and set in the east.
Scientists think a major crash with another object long ago might have flipped the planet.
Think about it: If we lived on Venus, our whole concept of east and west would be reversed. Compass directions would point the other way!
4. The Ancient Rock We Call Home
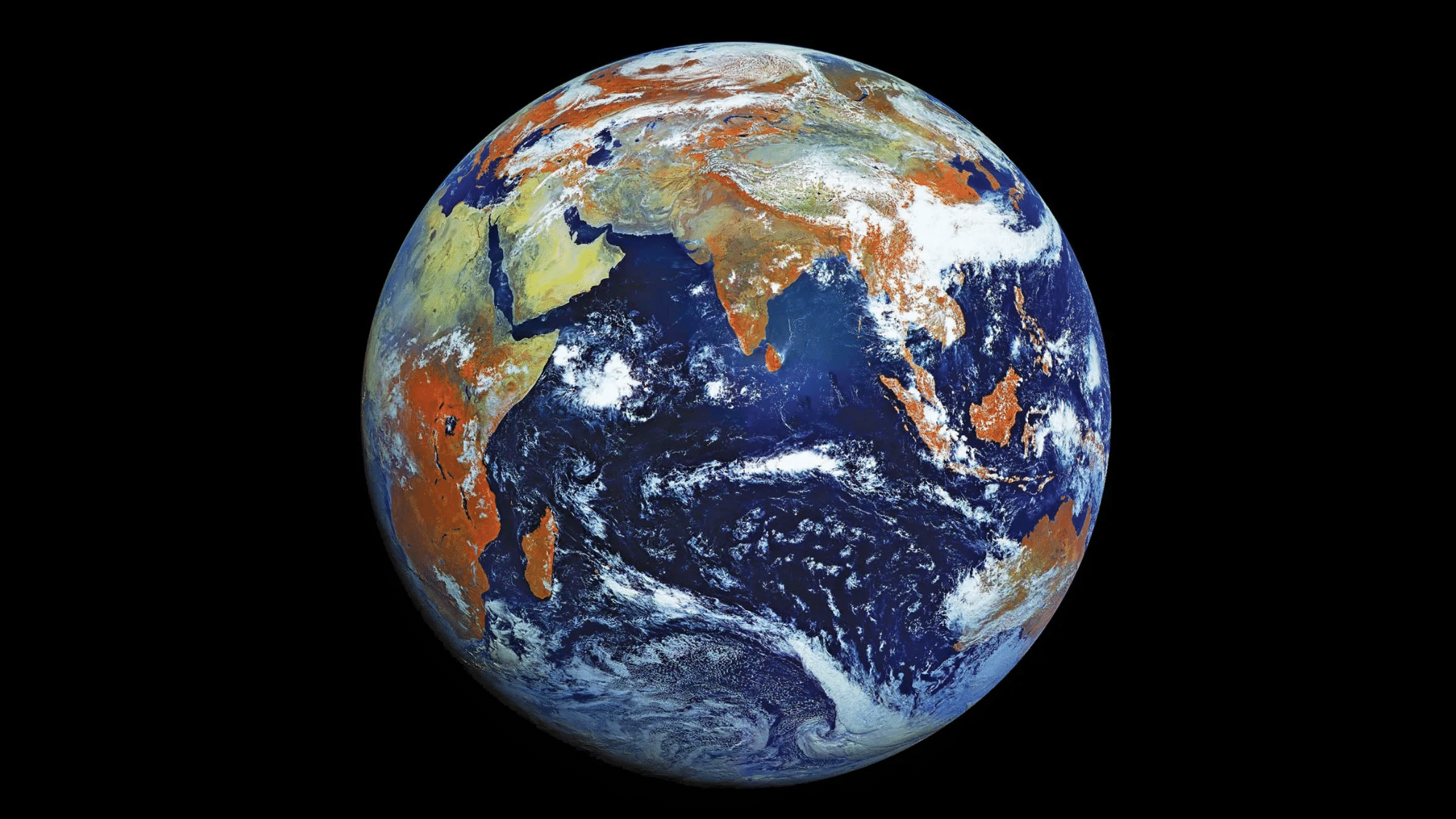
Earth has been spinning for 4.54 billion years!
To put that in perspective:
- If Earth’s history were a 24-hour day, humans would show up just 2 seconds before midnight
- Dinosaurs lived on Earth for 165 million years (we’ve been here for only 300,000)
- The first life forms appeared over 3.5 billion years ago
The rocks under your feet have seen continents split apart, oceans form and vanish, and countless species come and go.
5. The Planet-Eating Dust Monster
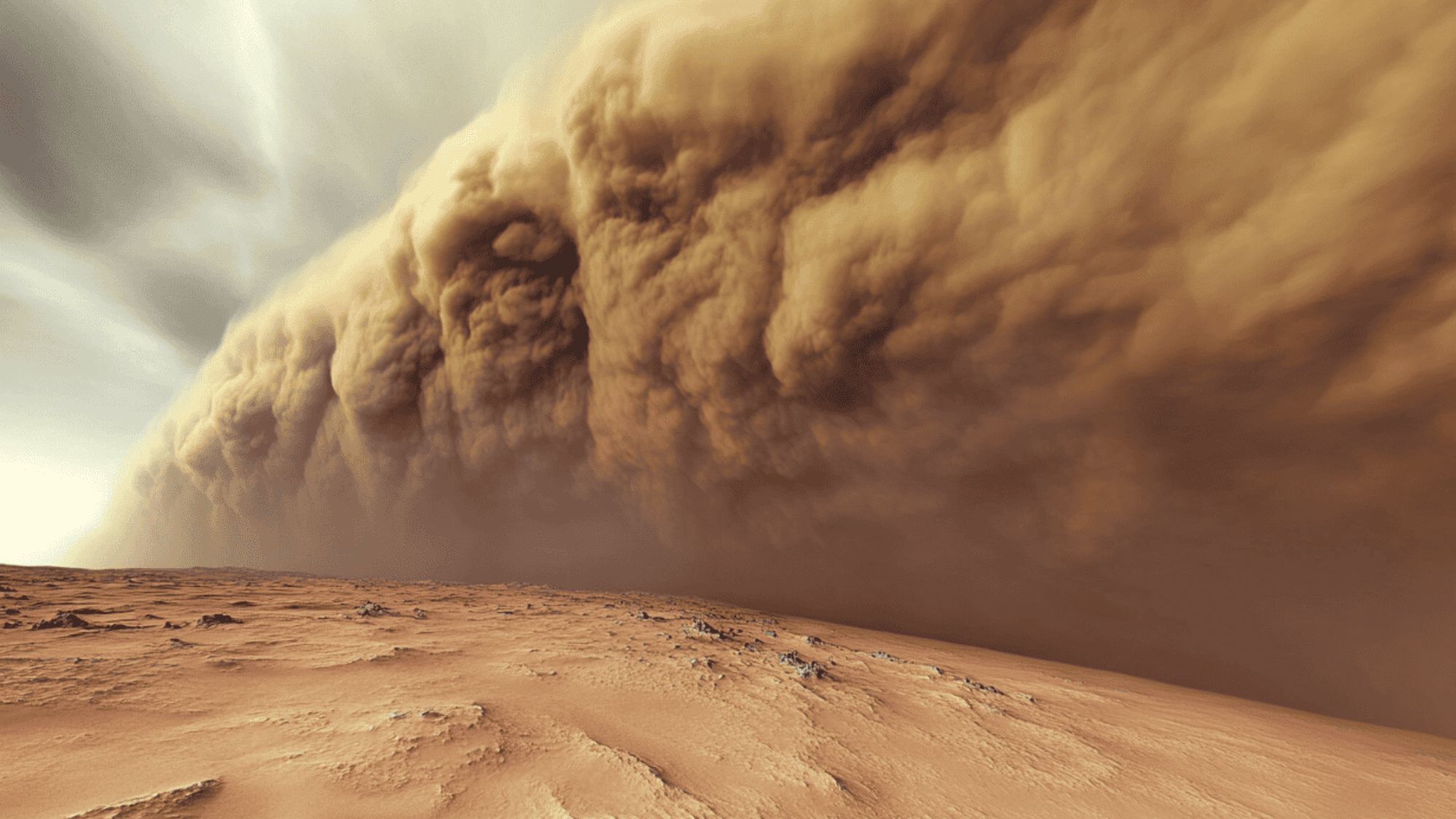

Did you ever hide from a rainstorm? On Mars, you would hide from dust for months!
Mars has dust storms so big they can:
- Cover the whole planet at once
- Last for months without stopping
- Block all sunlight from reaching the surface
- Lift dust more than 60 miles high
Mars rovers sometimes have to take long naps during these storms when their solar panels get too dusty to work.
6. The 400-Year Hurricane
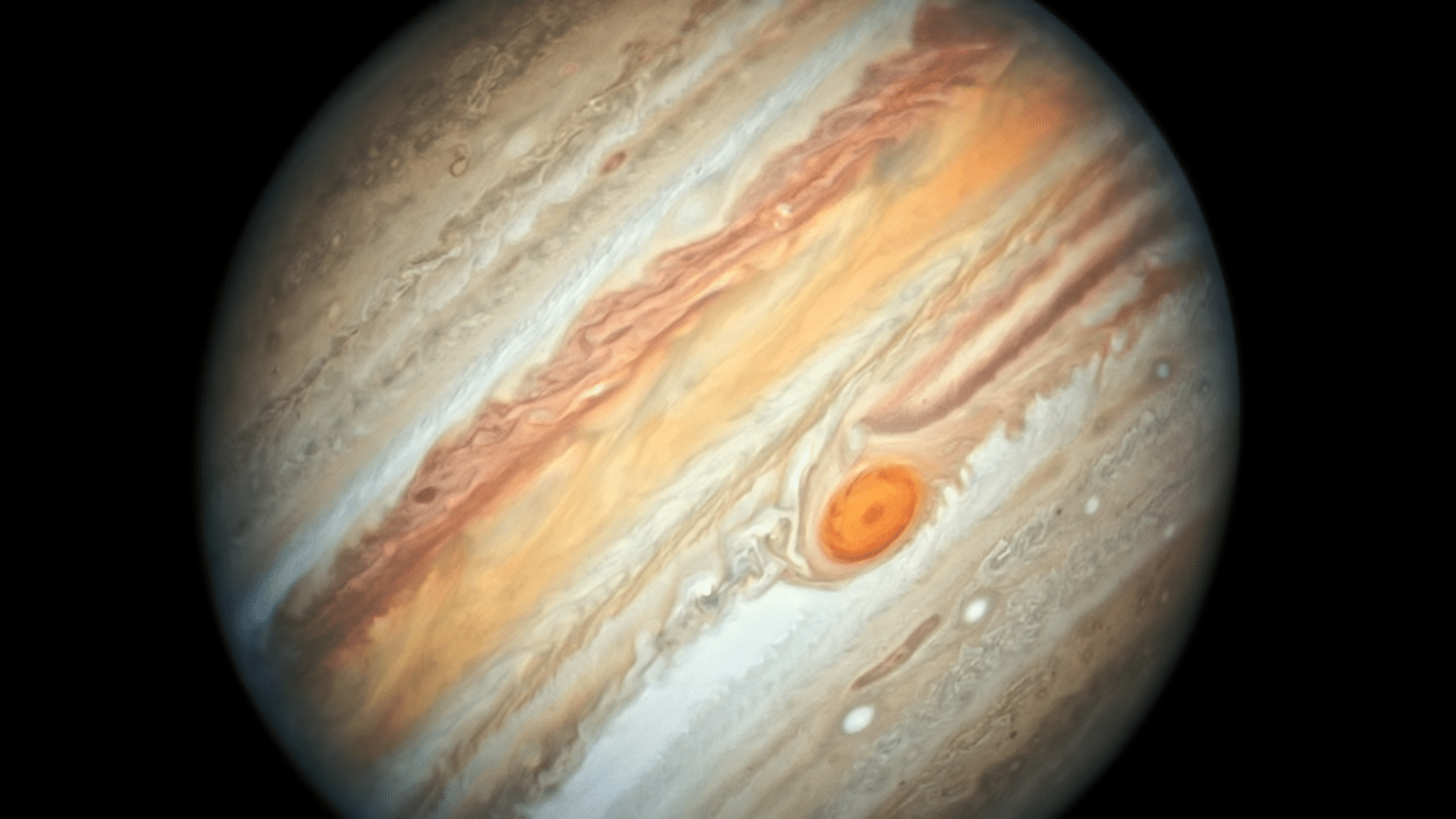

The spot on Jupiter that refuses to go away!
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot is:
- A storm that’s been going for at least 400 years
- So huge that three Earths could fit inside it
- Filled with winds faster than any on Earth
The longest storm on Earth lasted a month. Jupiter has been spinning since telescopes were first invented.
What if Earth had weather patterns that lasted centuries? We’d name hurricanes after historical periods instead of people.
7. The Not-So-Solid Rings
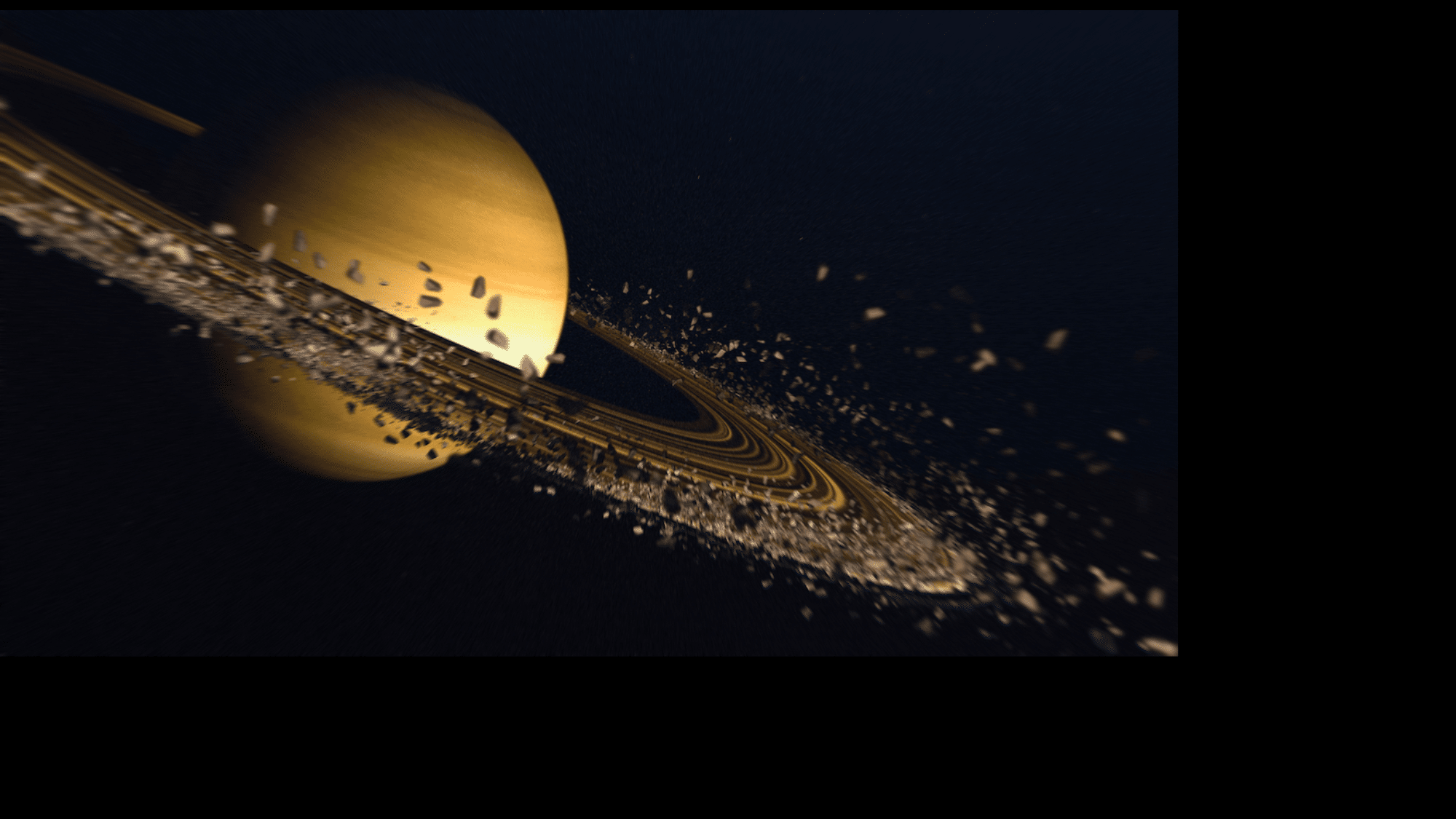

Saturn’s Secret: Those rings are full of holes!
Saturn’s beautiful rings look solid from a distance, but they are made of:
- Countless ice chunks
- Tiny dust bits
- Rocky pieces
- Objects from sand-sized to house-sized
If you could fly through the rings, you’d see millions of icy pieces, all orbiting Saturn like tiny moons.
The rings are huge (175,000 miles across) but paper-thin (mostly less than a mile thick). It’s like a CD the size of a city.
8. The Sideways Spinner
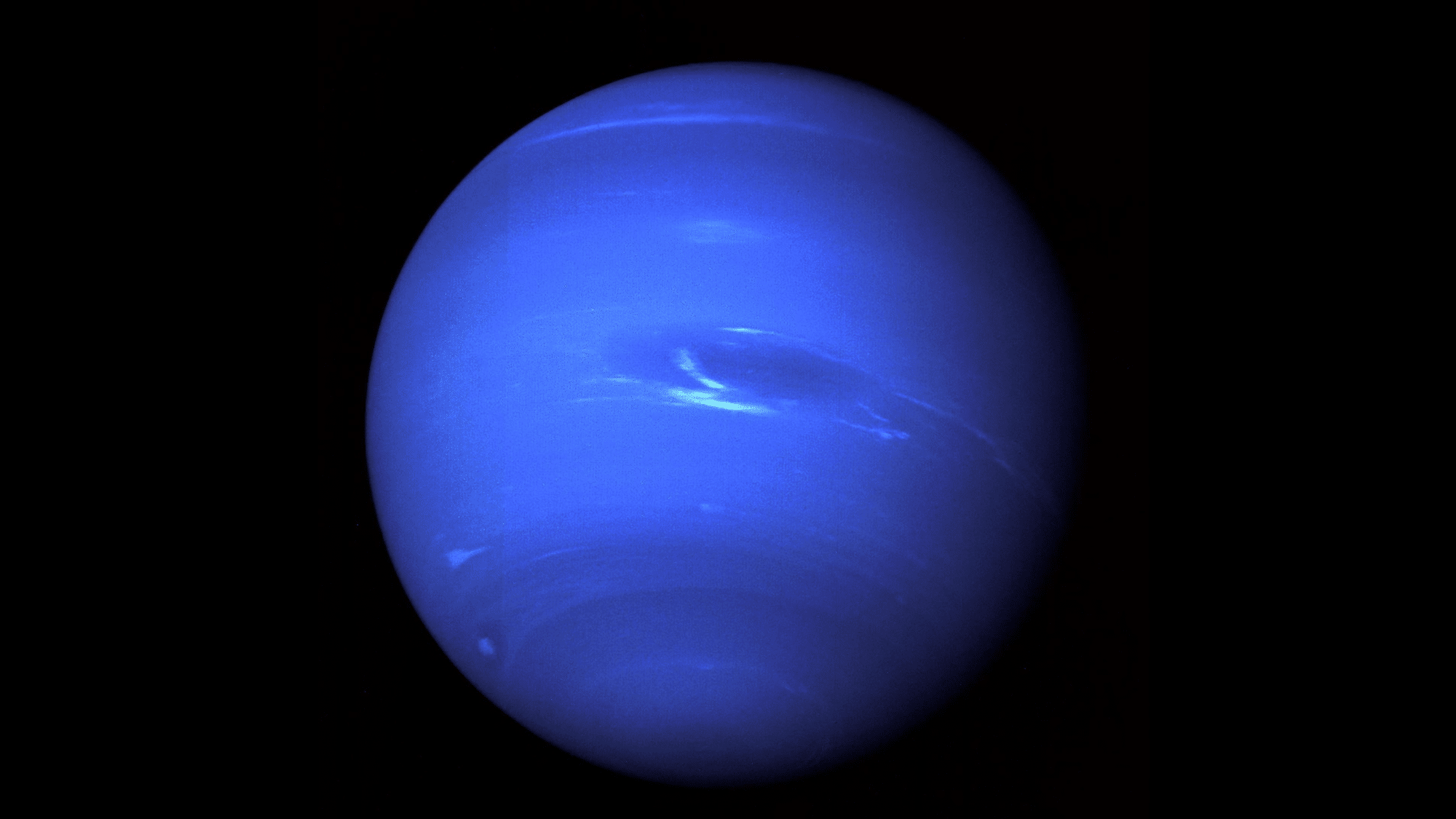
Uranus: The Planet That Rolls Instead of Spins!
Think of planets as spinning tops. Now imagine one top fell over and started rolling around the table instead, that’s Uranus!
Uranus tilts at 98 degrees, which means it:
- Rolls around the Sun like a ball
- Has seasons that last 21 Earth years
- Experiences 42 years of daylight, then 42 years of darkness at its poles
9. The Super-Speed Wind Champion
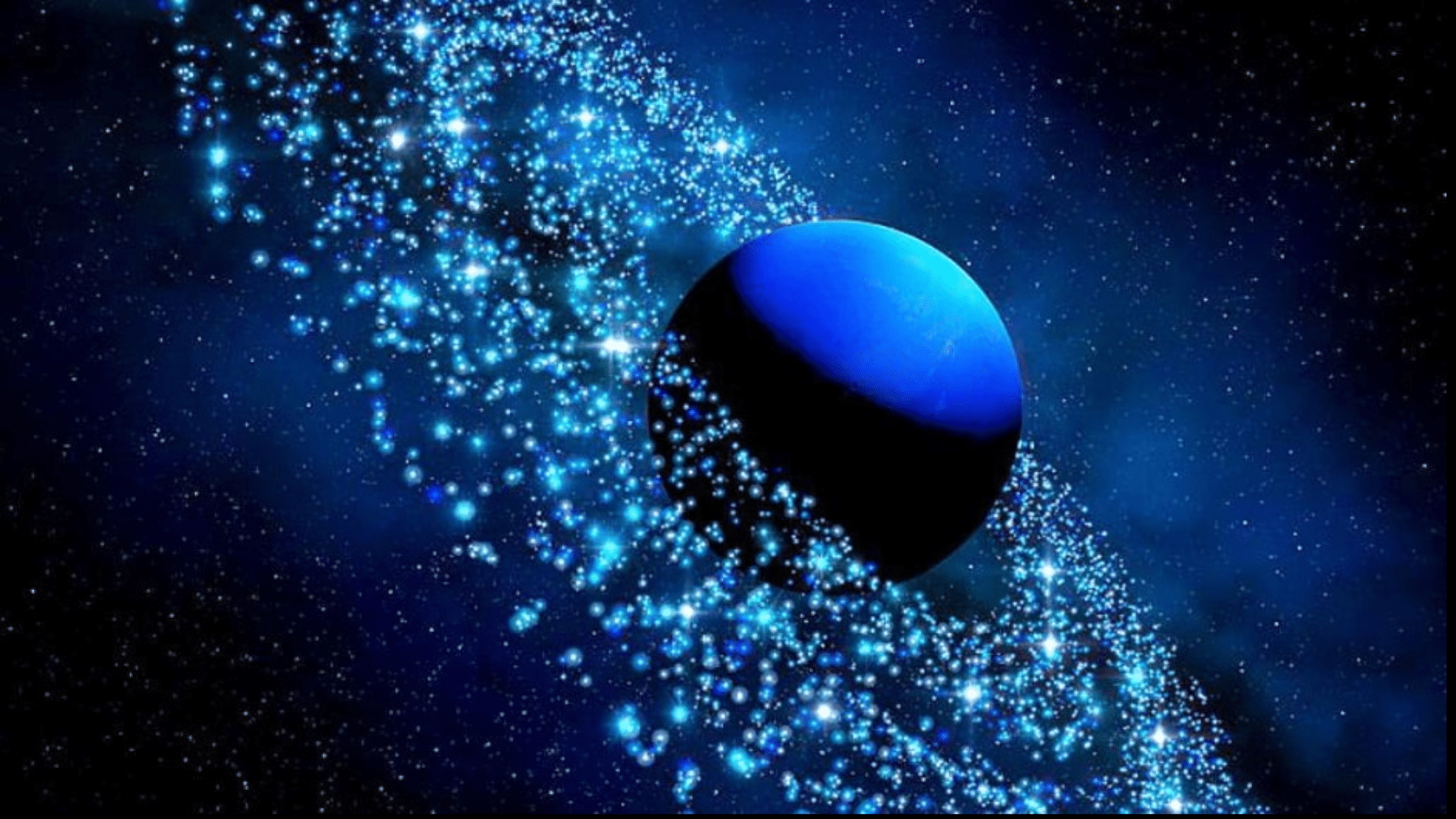

On Neptune, you would need more than an umbrella for bad weather!
- Wind speeds reach 1,200 miles per hour
- That’s 5 times faster than the worst hurricanes on Earth
- Fast enough to fly from New York to Los Angeles in 2 hours
These winds are even more surprising because Neptune sits so far from the Sun’s heat. The blue planet may look calm, but its skies are wild.
10. The Icy Heart of Pluto
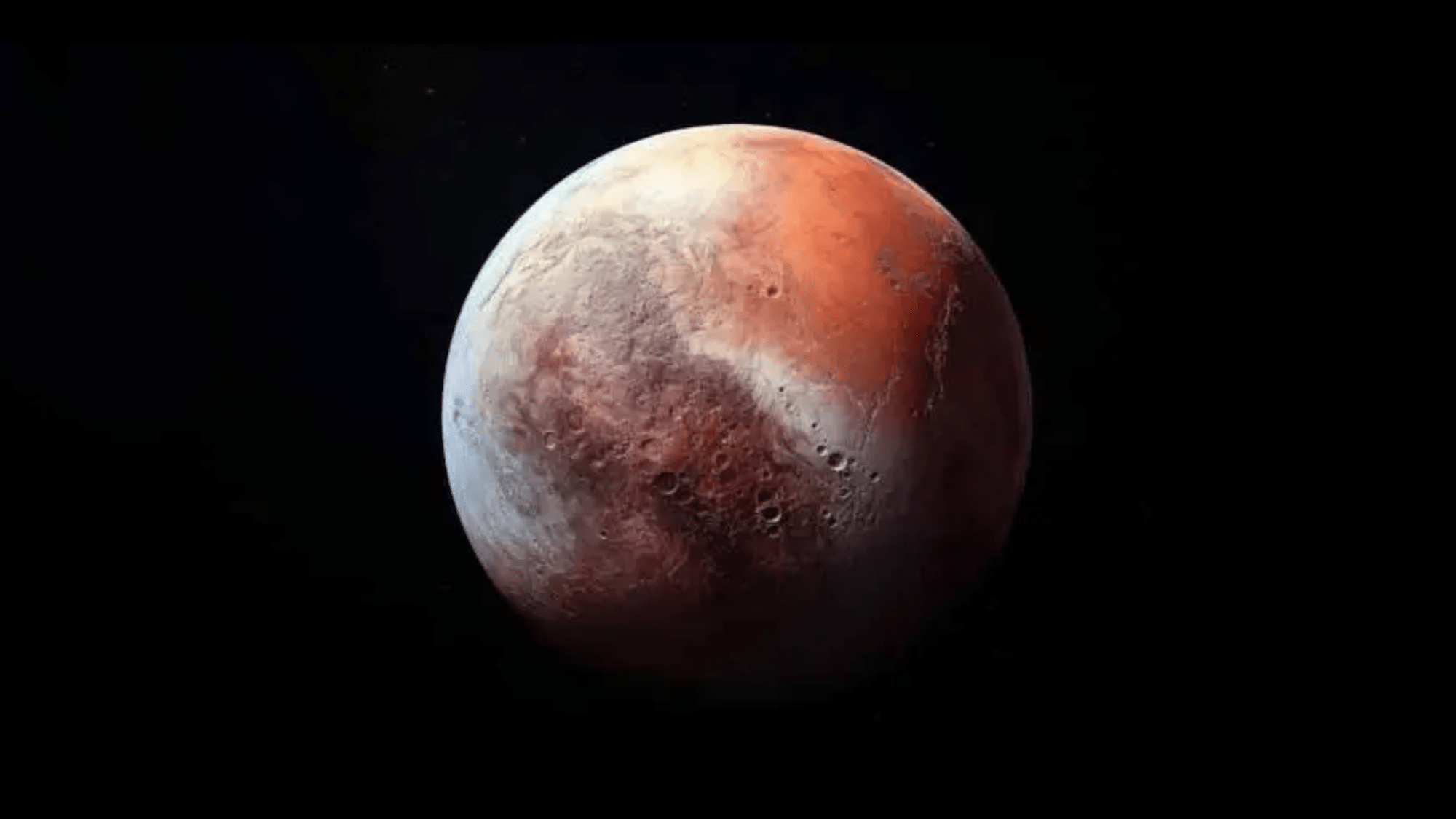

Pluto wears its heart on its surface. When the New Horizons spacecraft flew by Pluto in 2015, we all fell in love with the heart-shaped region on its surface:
- It’s called Tombaugh Regio (named after Pluto’s finder)
- Made of frozen nitrogen
- It stretches 1,000 miles across (about the size of Texas)
Before 2015, Pluto was only a tiny dot in our best telescopes. Now we know it has a heart.
11. The Light Time Machine

Starlight is a window to the past.
- Light from the nearest star (Proxima Centauri) takes 4.25 years to reach us
- Light travels at 186,000 miles each second
- Some stars we see today might not even exist anymore!
This means stargazing is a form of time travel. The light entering your eyes tonight began its trip when you were younger, maybe even before you were born.
12. The Cosmic Buddy System

If Earth orbited a double star system, we might see two suns in our sky, like that famous scene from Star Wars.
Days and nights would work differently, with complex patterns of light and shadow making for some wild sunrise and sunset combinations.
Fun fact: Over half the stars in our galaxy have stellar roommates:
- They come in pairs, triples, or even larger groups
- Some orbit so close they touch, others stay far apart
- Our Sun is unusual for being single
13. Star Factories Make Everything
The gold in rings and necklaces wasn’t made on Earth; it was created when giant stars exploded billions of years ago.
All elements heavier than iron formed in:
- The final moments of large stars
- The massive heat of star explosions
- The crash of dense stars remains
14. Our Big Home Address

If you could travel at light speed (the fastest possible speed), it would still take 100,000 years to cross from one side of the Milky Way Galaxy to the other.
Our galaxy contains:
- 100-400 billion stars
- A span of 100,000 light-years across
- Our Sun, plus countless other solar systems
15. Galactic Neighbourhoods

From the southern half of Earth, you can spot our two closest galaxy neighbors, the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds, with your naked eye on clear nights.
These galaxy groups slowly dance around each other over billions of years, pulled by gravity into cosmic communities.
Just like stars group together, galaxies form their own clubs:
- Our Milky Way belongs to the “Local Group.”
- This group has over 54 galaxies of all sizes
- The nearest large galaxies can be seen without telescopes
16. The Cosmic Magnifying Glass

Black holes bend light like giant lenses. Black holes pull so strongly that they can:
- Curve light paths around them
- Make distant stars visible that would otherwise be hidden
- Create multiple images of the same star
This light-bending effect helps scientists study far-off parts of space that would otherwise be impossible to see.
It’s like the black hole creates natural telescopes in space, bringing the unseen into view through its immense pull.
17. The Monster in Space

Meet TON 618: The heavyweight champion of black holes. This black hole is so big that:
- It equals 66 billion Suns in mass
- It could swallow our entire solar system without notice
- Scientists still don’t fully understand how it grew so large
If we placed this giant in our solar system, it would sit there like a cosmic vacuum cleaner, pulling in everything around it.
Black holes like TON 618 show just how extreme objects in space can become, growing over billions of years by eating stars and merging with other black holes.
18. The Silent Universe

Space is where no one can hear you scream. In movies, space explosions make loud booms. In real space:
- You would see the explosion
- Feel the heat (if close enough)
- But you would hear nothing at all
Without air or other materials to carry sound waves, space remains completely silent. Astronauts can only hear each other through radio systems in their helmets.
Communication in space must occur through light, radio waves, or direct contact, never through sound like we’re used to on Earth.
19. Not-So-Empty Space

Space isn’t completely empty. Between stars and planets, space contains:
- Tiny dust particles
- Scattered gas atoms
- Various forms of energy
- Invisible matter, we’re still trying to understand
Most of the space is what scientists call a hard vacuum, but not perfectly empty. In some regions, you might find only a few atoms per cubic meter, spread out extremely, but still present.
Floating through such almost-emptiness would feel strange, with nothing solid for millions of miles, yet not truly being in complete nothingness.
20. The Great Cosmic Web
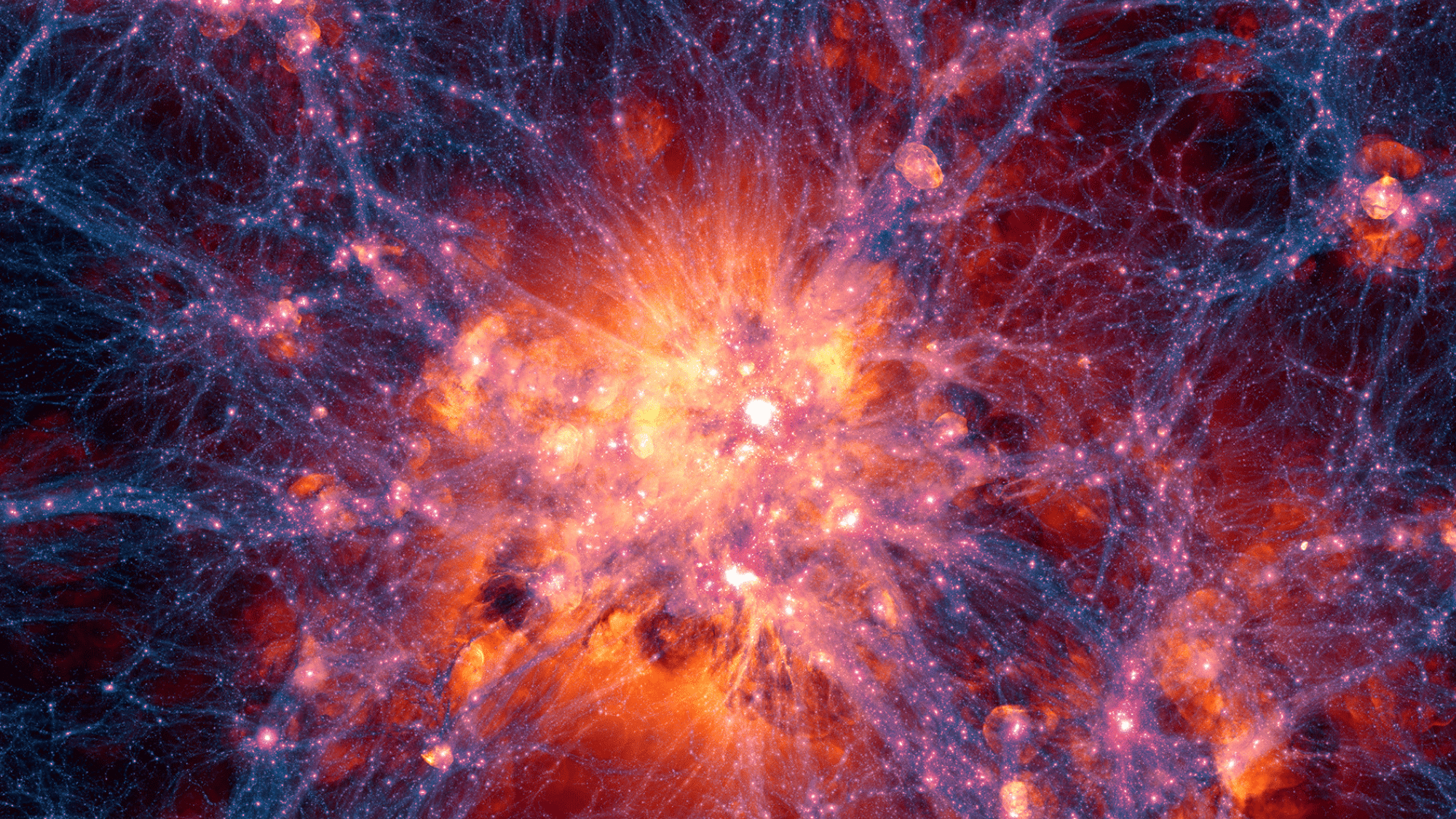
Galaxies form the biggest pattern in nature. Instead of spreading evenly through space, galaxies form:
- Long strings of galaxy clusters
- Huge empty bubbles called voids
- A pattern that looks like a giant spider web
The empty spaces between galaxy strings can be hundreds of millions of light-years across truly enormous bubbles of almost nothing.
This web pattern formed from tiny differences in how matter was spread right after the Big Bang, growing over billions of years into the largest structure we know of.
21. The Smell of Outer Space

Astronauts say space has a scent. When space walkers return to their ships, their suits often smell like:
- Seared steak
- Hot metal
- Welding fumes
Space itself has no smell (it’s a vacuum), but particles that stick to suits during spacewalks bring these scents back inside.
These odors likely come from energy reactions when atoms from the suits mix with space radiation. It’s one of those small, human details about space travel that you rarely hear about!
22. The Moonwalk (Away From Earth)

The Moon moves about 1.5 inches away from Earth each year because:
- Moon’s gravity pulls on Earth’s oceans
- This creates tides that slightly slow the Earth’s spin
- The energy transfer pushes the Moon outward
When Earth first formed, the Moon was much closer and would have looked much bigger in the sky. Future humans will see a smaller Moon than we do today.
23. The Deep Freeze of Space
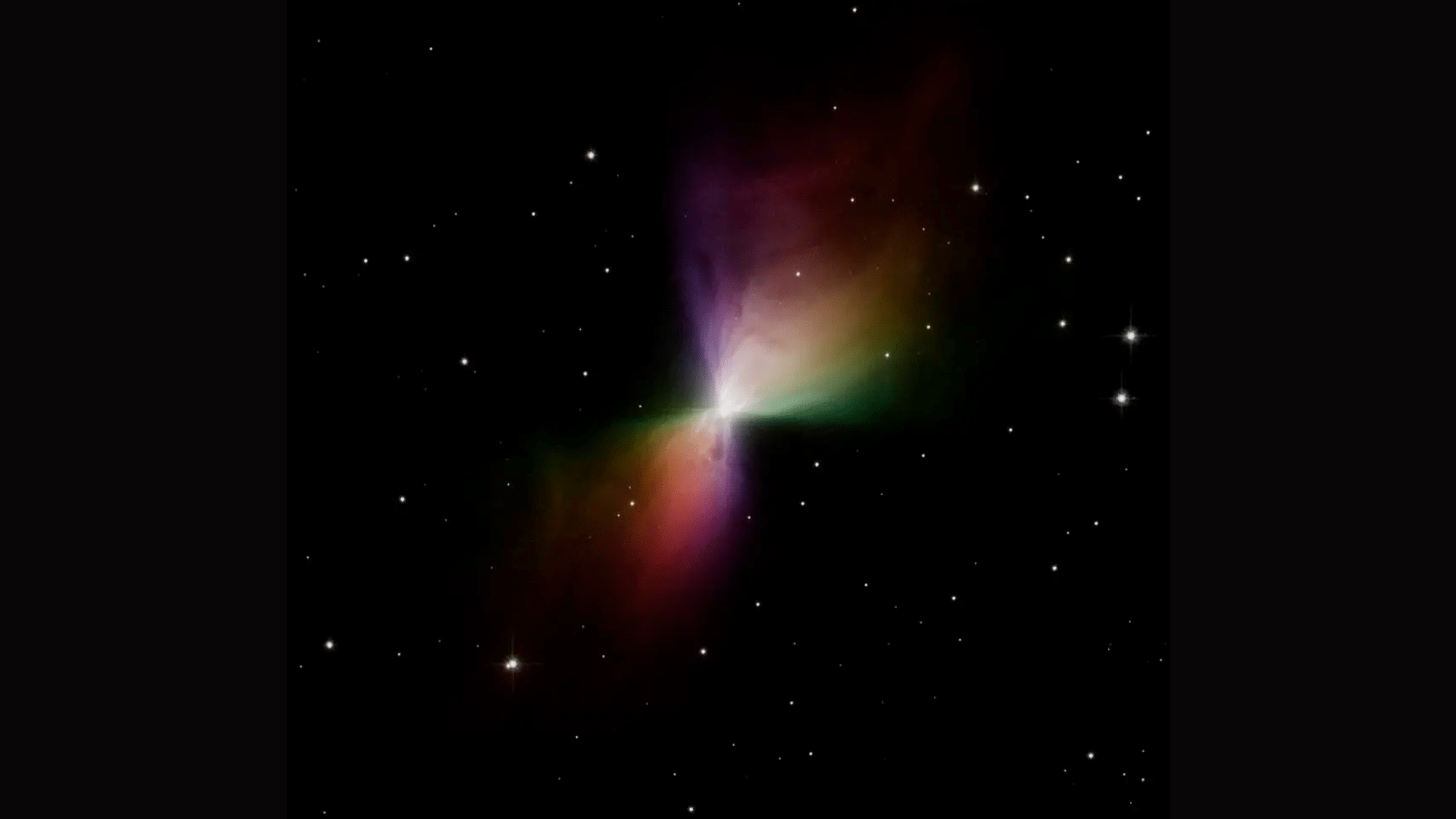
The Boomerang Nebula: Colder than your freezer could ever be. This nebula holds the record for the coldest known spot in space:
- Just 1 degree above absolute zero (-459.67°F or -273.15°C)
- Colder than the background temperature of the universe
- At this temperature, atoms barely move at all
For comparison:
- Your freezer: About 0°F (-18°C)
- Antarctica’s lowest record: -128.6°F (-89.2°C)
- Boomerang Nebula: -458°F (-272°C)
This super-cold nebula formed when a dying star sent out gas that grew colder as it expanded, like how spray from a can feels cold.
24. The Color-Flipped Sunset
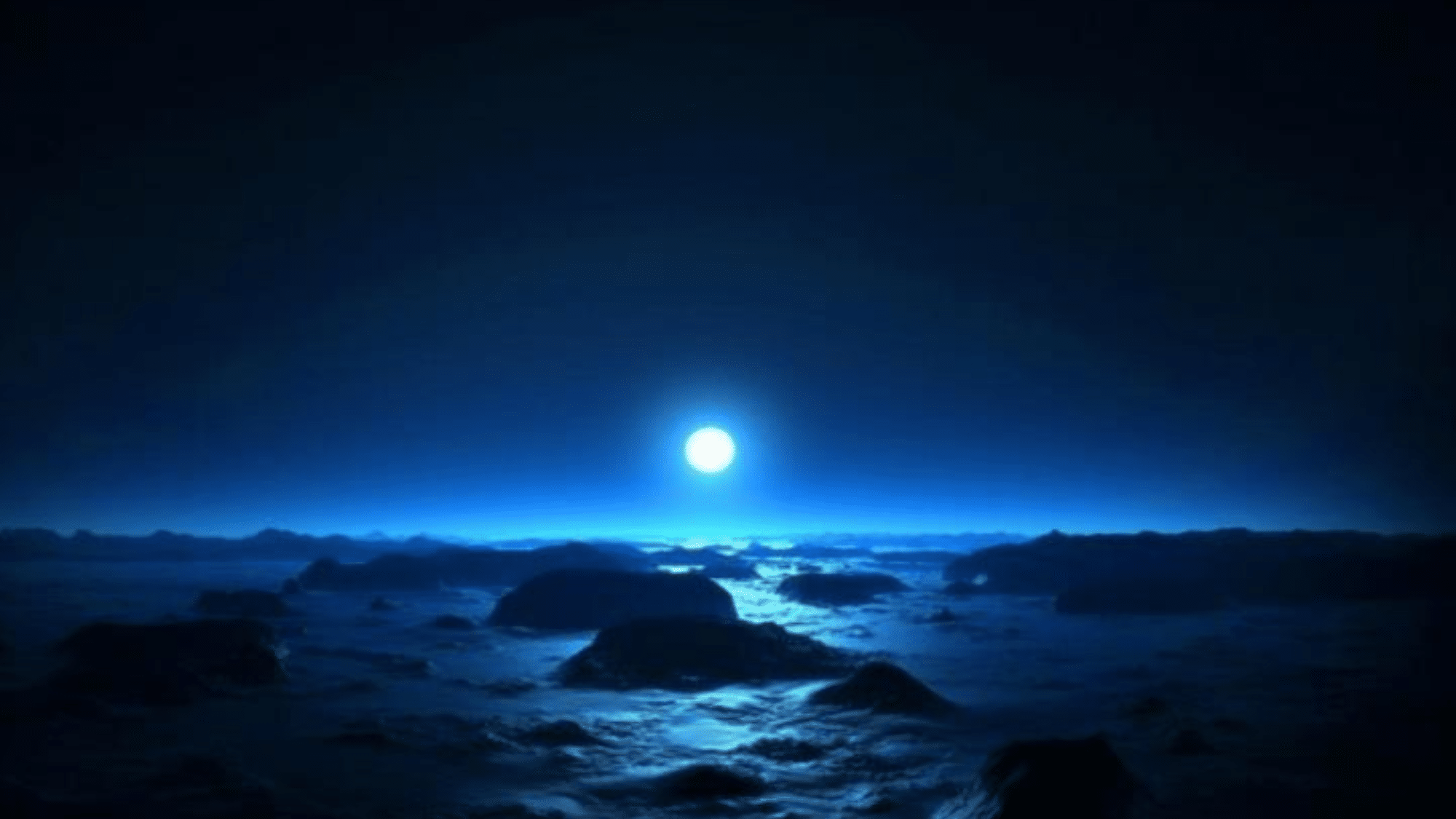

On Mars, sunsets are blue instead of red. While Earth sunsets show warm red and orange colors, Mars sunsets appear in cool blue tones because:
- Fine dust in Mars’ thin air scatters light differently
- Blue light gets through while red light scatters away
- The exact opposite of what happens on Earth!
Rovers like Spirit and Opportunity have sent back photos of these unusual sunsets, showing how even something as basic as sunset colors can be completely different on another world.
25. Martian Water Slides
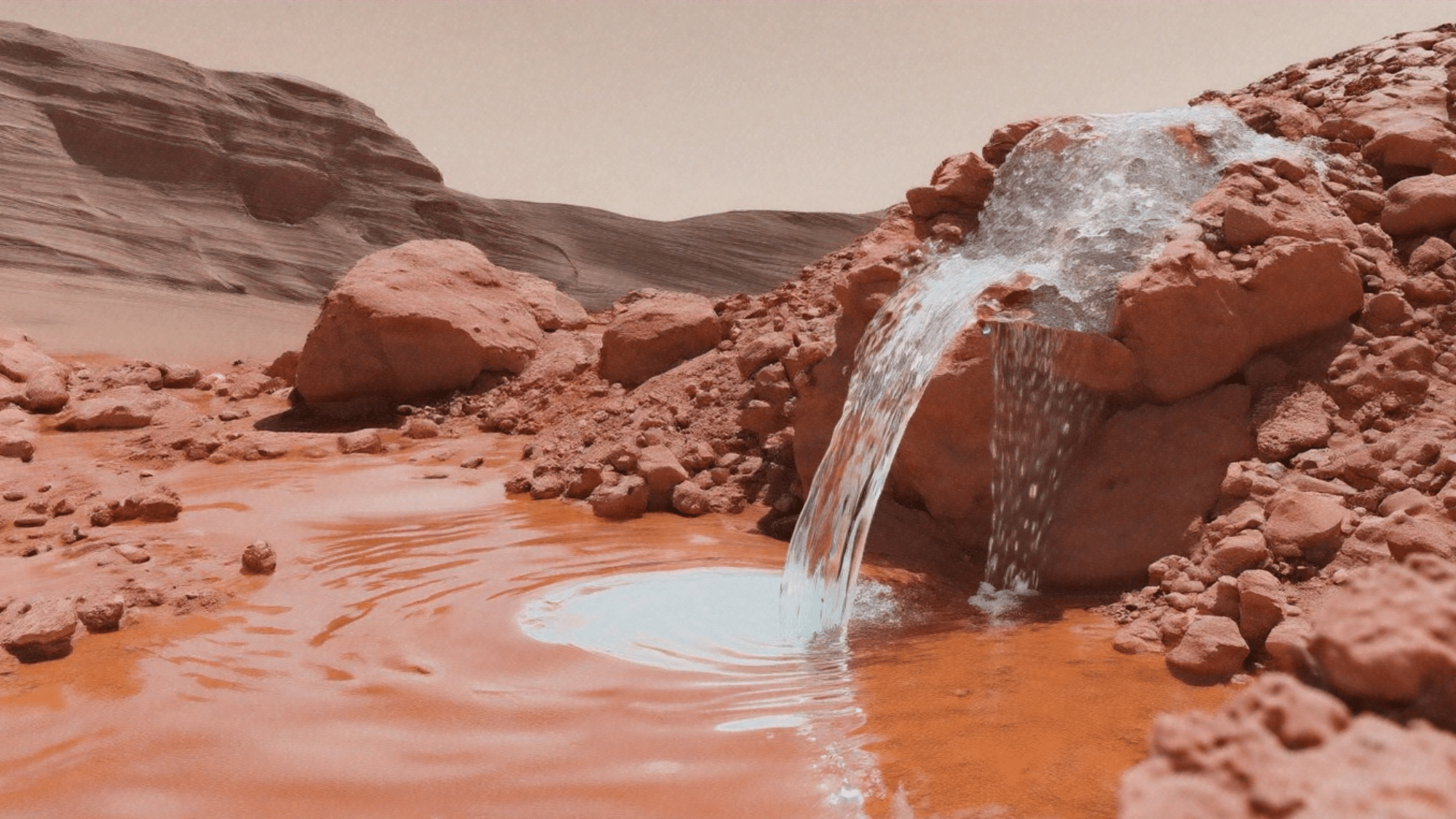

Mars has liquid water, but you wouldn’t want to drink it. Scientists have found signs that water still flows on Mars today:
- It appears as dark streaks on some slopes
- These streaks grow longer in warm seasons
- The water is extremely salty, like super-strong brine
This salty water can stay liquid in Mars’ harsh conditions instead of freezing or turning to vapor.
While this water might be too salty for Earth-like life, it opens the possibility that some form of life could exist on Mars, changing how we think about our neighbor planet.
26. Space Water Bubbles
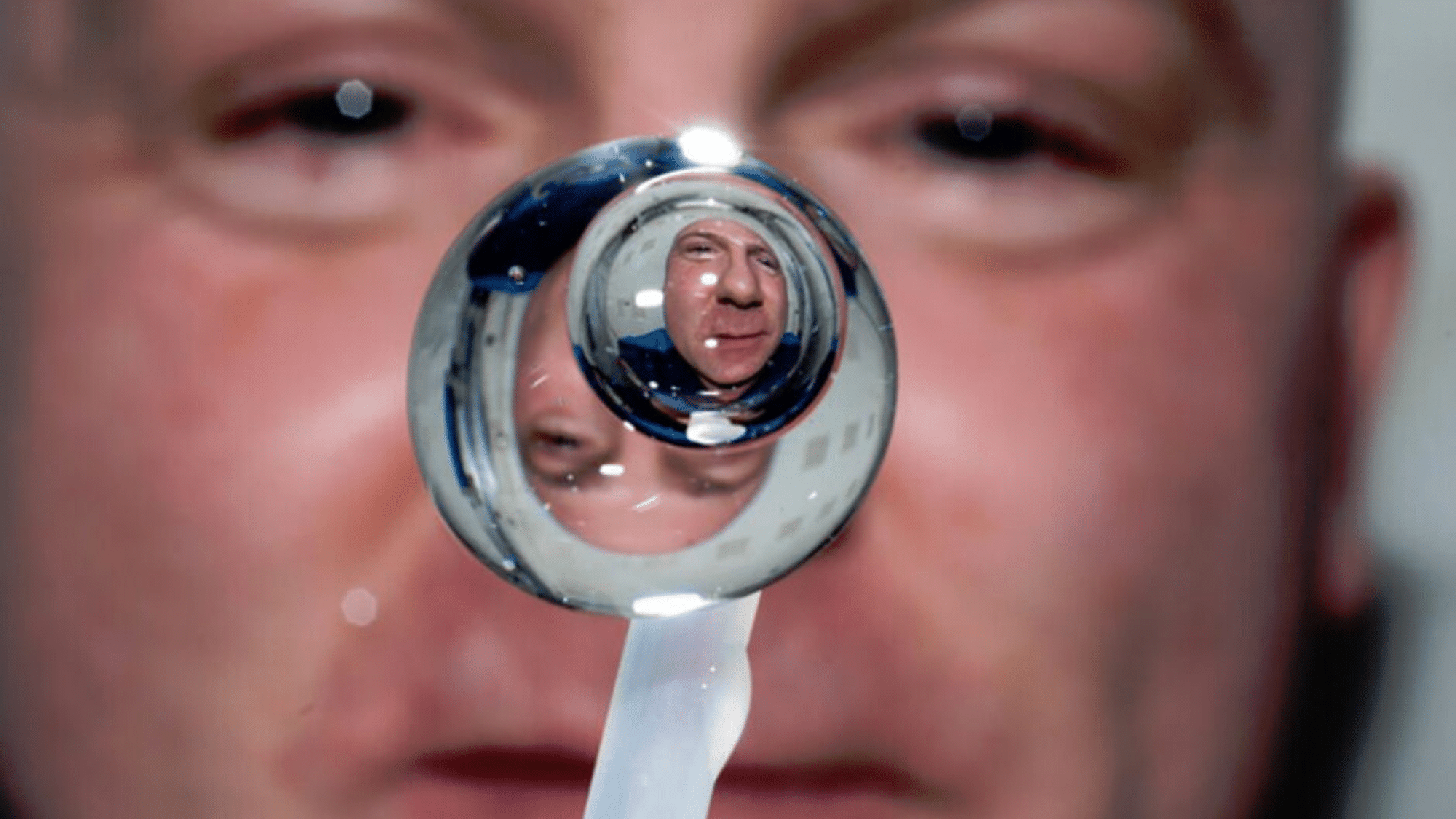

In space, water doesn’t flow; it floats. Without gravity pulling it down, water in space:
- Form perfect spheres that float around
- Sticks to itself through surface tension
- Can be pushed into different shapes, but always returns to a sphere
Space station astronauts often play with these floating water drops, watching them wobble, merge, and split.
This unusual water behavior necessitates the use of special straws and sealed containers for drinks among space travelers. Even simple acts like washing your hands or brushing your teeth become totally different in space.
27. Wishes on Space Dust
Falling stars are tiny rocks burning up. When you see a streak of light zip across the night sky:
- It’s usually a piece of rock or dust the size of a grain of sand
- It’s moving at speeds up to 160,000 mph
- It heats up from friction with the Earth’s air
- The bright streak lasts just seconds as it burns away
People across cultures have made wishes on these brief flashes for thousands of years.
28. The Ever-Growing Universe
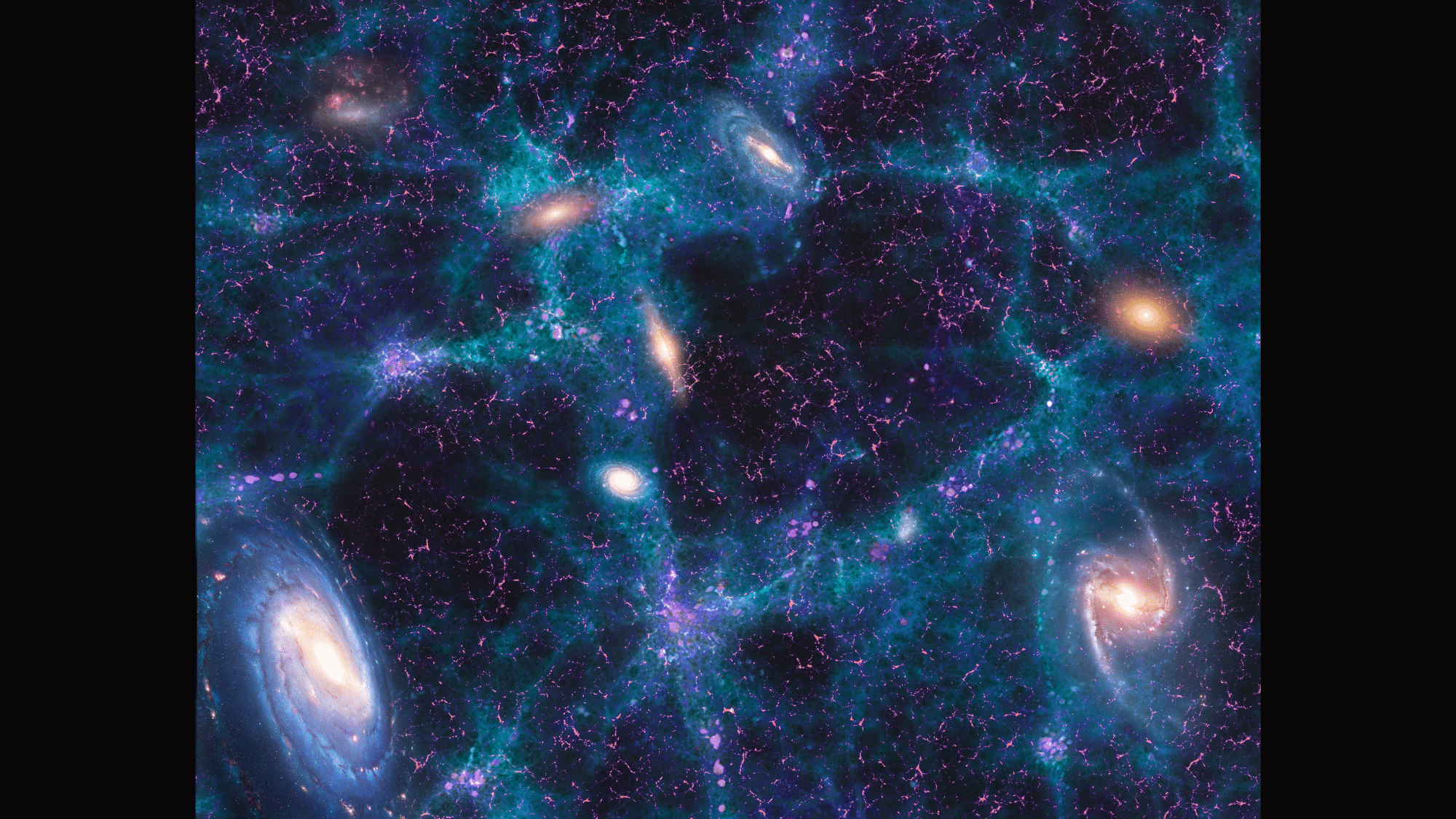

Our universe is like a balloon that keeps inflating. The universe grows bigger all the time, and this growth is speeding up:
- Far-off galaxies move away faster than closer ones
- Space itself stretches like the surface of an inflating balloon
- Some galaxies now move away faster than the speed of light due to this stretching
Scientists discovered this growth by studying light from distant stars, which showed that space itself was expanding.
This continuing growth raises big questions about our universe’s future. Will it expand forever or eventually stop?
29. Your Cosmic Ancestry
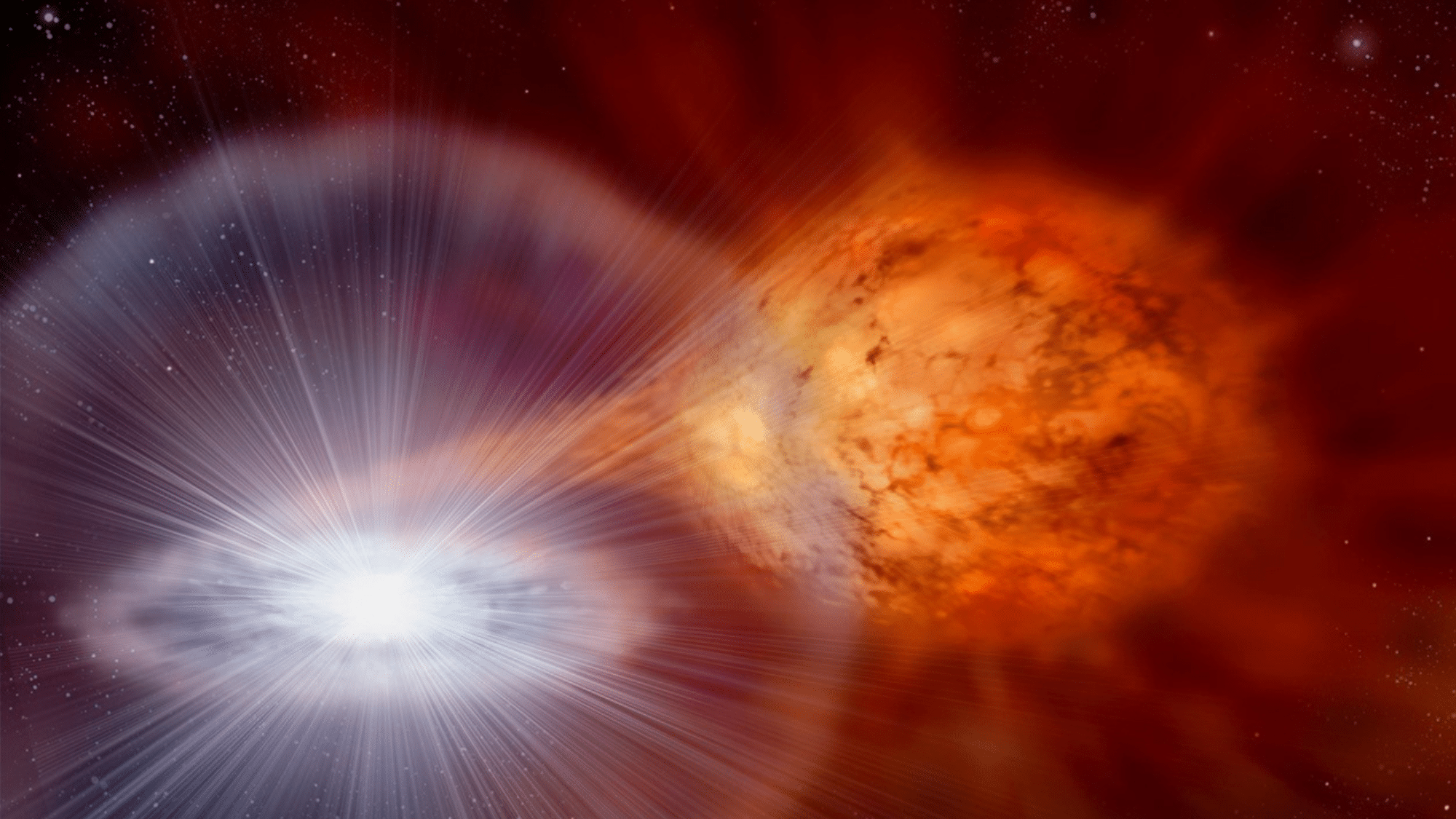
You are made of star ingredients! Almost everything in your body was created inside ancient stars:
- The carbon in your cells
- The calcium in your bones
- The iron in your blood
When those stars died billions of years ago, they scattered these elements into space, which later became part of Earth and eventually us.
Next time you look up at the night sky, remember: you’re not just observing distant lights, you’re looking at your cosmic family tree!
In Conclusion
Looking up at the stars makes us wonder about our place in the universe.
These space facts show us how small yet linked we are to the cosmos around us.
Want to learn more? Check out space websites or grab a book from your local library.
You might even want to join a star-gazing club in your area!
Share your favorite space fact in the comments below.